The effect of standard dose multivitamin supplementation on disease progression in HIV-infected adults initiating HAART: a randomized double blind placebo-controlled trial in Uganda
- PMID: 26285704
- PMCID: PMC4545778
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-015-1082-x
The effect of standard dose multivitamin supplementation on disease progression in HIV-infected adults initiating HAART: a randomized double blind placebo-controlled trial in Uganda
Abstract
Background: Efficacy trials investigating the effect of multivitamin (MV) supplementations among patients on Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) have so far been inconclusive. We conducted a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial to determine the effect of one recommended daily allowance (RDA) of MV supplementation on disease progression in patients initiating HAART.
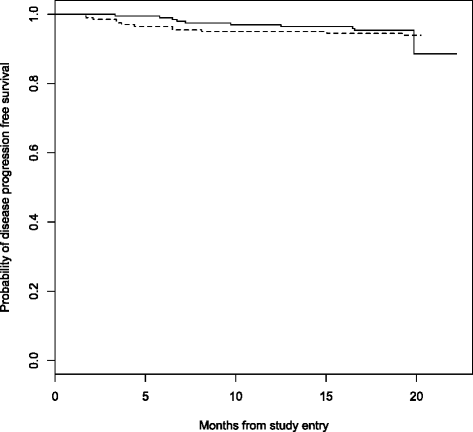
Methods: Eligible subjects were randomized to receive placebo or MV supplementation including vitamins B-complex, C and E. Participants were followed for up to 18 months. Primary endpoints were: change in CD4 cell count, weight and quality of life (QoL). Secondary endpoints were: i) development of a new or recurrent HIV disease progression event, including all-cause mortality; ii) switching from first- to second-line antiretroviral therapy (ART); and iii) occurrence of an adverse event. Intent-to-treat analysis, using linear regression mixed effects models were used to compare changes over time in the primary endpoints between the study arms. Kaplan-Meier time-to-event analysis and the log-rank test was used to compare HIV disease progression events and all-cause mortality.
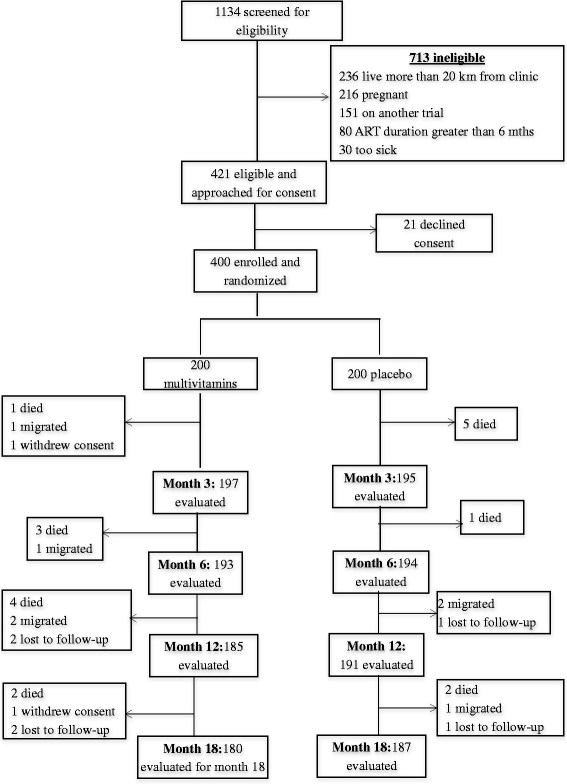
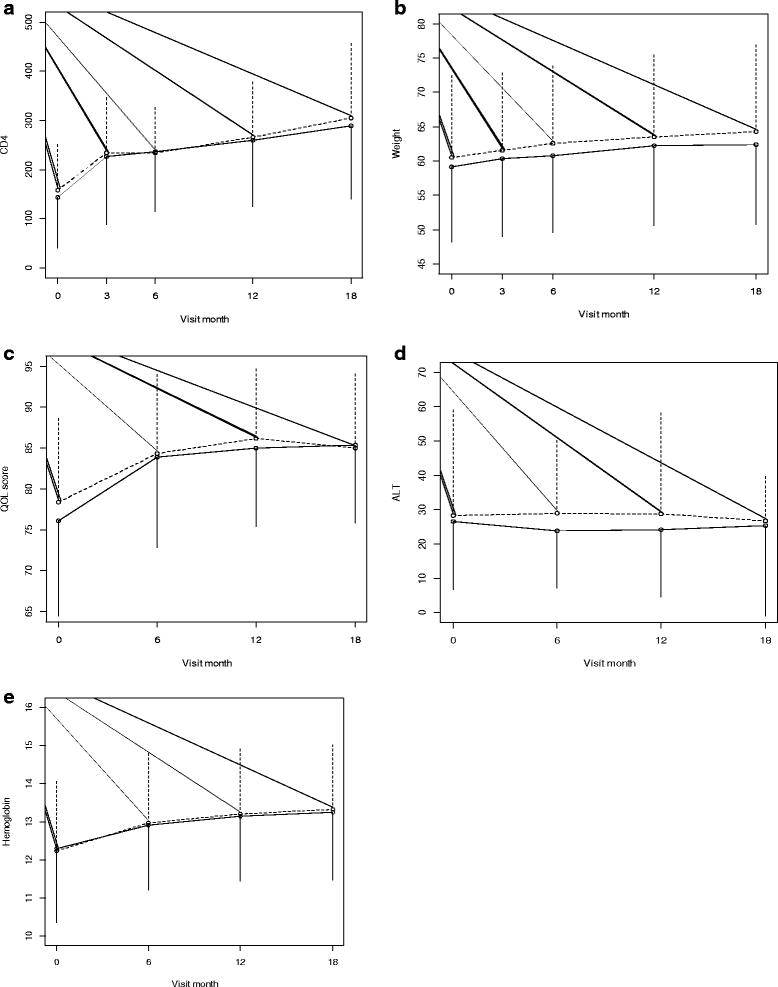
Results: Four hundred participants were randomized, 200 onto MV and 200 onto placebo. By month 18, the average change in CD4 cell count in the MV arm was 141 cells/uL compared to 147 cells/uL in the placebo arm, a mean difference of -6 · 17 [95 % CI -29 · 3, 16 · 9]. The average change in weight in the MV arm was 3 · 9 kg compared to 3 · 3 kg in the placebo arm, a mean difference of 0 · 54 [95 % CI -0 · 40, 1 · 48]; whereas average change in QoL scores in the MV arm was 6 · 8 compared to 8 · 8 in the placebo arm, a mean difference of -2.16 [95 % CI -4 · 59,0 · 27]. No significant differences were observed in these primary endpoints, or in occurrence of adverse events between the trial arms.
Conclusions: One RDA of MV supplementation was safe but did not have an effect on indicators of disease progression among HIV infected adults initiating HAART.
Trial registration: Clinical trials NCT01228578 , registered on 15th October 2010.
Figures
References
-
- Beisel WR. In: Nutrition and immunology: principles and practices. Gershwin ME, German JB, Keen CL, editors. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2000. pp. 389–403.
-
- Beisel WR. Single nutrients and immunity. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982;35(2 Suppl):417–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

