Molgenis-impute: imputation pipeline in a box
- PMID: 26286716
- PMCID: PMC4541731
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-015-1309-3
Molgenis-impute: imputation pipeline in a box
Abstract
Background: Genotype imputation is an important procedure in current genomic analysis such as genome-wide association studies, meta-analyses and fine mapping. Although high quality tools are available that perform the steps of this process, considerable effort and expertise is required to set up and run a best practice imputation pipeline, particularly for larger genotype datasets, where imputation has to scale out in parallel on computer clusters.
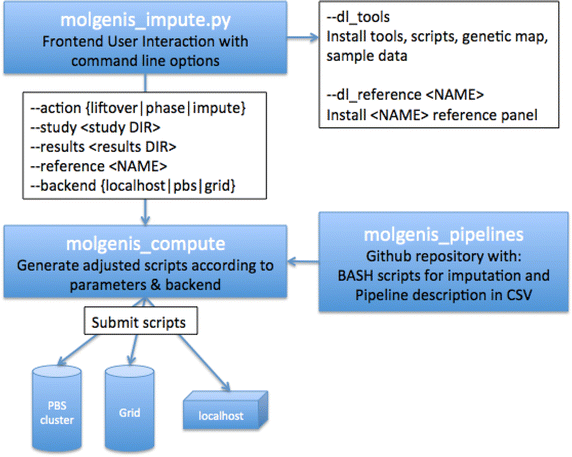
Results: Here we present MOLGENIS-impute, an 'imputation in a box' solution that seamlessly and transparently automates the set up and running of all the steps of the imputation process. These steps include genome build liftover (liftovering), genotype phasing with SHAPEIT2, quality control, sample and chromosomal chunking/merging, and imputation with IMPUTE2. MOLGENIS-impute builds on MOLGENIS-compute, a simple pipeline management platform for submission and monitoring of bioinformatics tasks in High Performance Computing (HPC) environments like local/cloud servers, clusters and grids. All the required tools, data and scripts are downloaded and installed in a single step. Researchers with diverse backgrounds and expertise have tested MOLGENIS-impute on different locations and imputed over 30,000 samples so far using the 1,000 Genomes Project and new Genome of the Netherlands data as the imputation reference. The tests have been performed on PBS/SGE clusters, cloud VMs and in a grid HPC environment.
Conclusions: MOLGENIS-impute gives priority to the ease of setting up, configuring and running an imputation. It has minimal dependencies and wraps the pipeline in a simple command line interface, without sacrificing flexibility to adapt or limiting the options of underlying imputation tools. It does not require knowledge of a workflow system or programming, and is targeted at researchers who just want to apply best practices in imputation via simple commands. It is built on the MOLGENIS compute workflow framework to enable customization with additional computational steps or it can be included in other bioinformatics pipelines. It is available as open source from: https://github.com/molgenis/molgenis-imputation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

