Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells
- PMID: 26286986
- PMCID: PMC4568231
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1513426112
Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells
Abstract
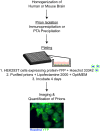
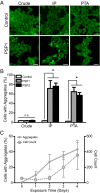
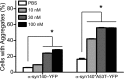
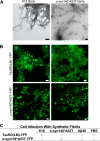
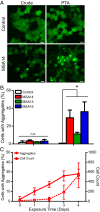
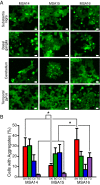
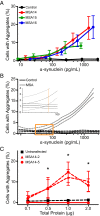
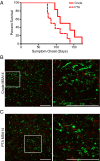
Increasingly, evidence argues that many neurodegenerative diseases, including progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), are caused by prions, which are alternatively folded proteins undergoing self-propagation. In earlier studies, PSP prions were detected by infecting human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells expressing a tau fragment [TauRD(LM)] fused to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). Here, we report on an improved bioassay using selective precipitation of tau prions from human PSP brain homogenates before infection of the HEK cells. Tau prions were measured by counting the number of cells with TauRD(LM)-YFP aggregates using confocal fluorescence microscopy. In parallel studies, we fused α-synuclein to YFP to bioassay α-synuclein prions in the brains of patients who died of multiple system atrophy (MSA). Previously, MSA prion detection required ∼120 d for transmission into transgenic mice, whereas our cultured cell assay needed only 4 d. Variation in MSA prion levels in four different brain regions from three patients provided evidence for three different MSA prion strains. Attempts to demonstrate α-synuclein prions in brain homogenates from Parkinson's disease patients were unsuccessful, identifying an important biological difference between the two synucleinopathies. Partial purification of tau and α-synuclein prions facilitated measuring the levels of these protein pathogens in human brains. Our studies should facilitate investigations of the pathogenesis of both tau and α-synuclein prion disorders as well as help decipher the basic biology of those prions that attack the CNS.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; multiple system atrophy; neurodegeneration; strains; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Parkinson J. An Essay on the Shaking Palsy. Sherwood, Neely, and Jones; London: 1817.
-
- Forster E, Lewy FH. Paralysis agitans. In: Lewandowsky M, editor. Pathologische Anatomie. Handbuch der Neurologie. Springer; Berlin: 1912. pp. 920–933.
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, et al. Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Singleton AB, et al. α-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science. 2003;302(5646):841. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin MC, et al. Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2004;364(9440):1167–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG002132/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002132/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008151/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG031220/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG010770/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG021601/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG021601/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG031220/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG010770/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG19724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

