Structure-Based Optimization of Inhibitors of the Aspartic Protease Endothiapepsin
- PMID: 26287174
- PMCID: PMC4581293
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160819184
Structure-Based Optimization of Inhibitors of the Aspartic Protease Endothiapepsin
Abstract
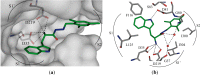
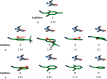
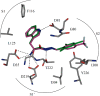
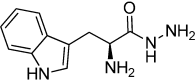
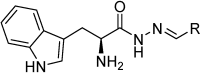
Aspartic proteases are a class of enzymes that play a causative role in numerous diseases such as malaria (plasmepsins), Alzheimer's disease (β-secretase), fungal infections (secreted aspartic proteases), and hypertension (renin). We have chosen endothiapepsin as a model enzyme of this class of enzymes, for the design, preparation and biochemical evaluation of a new series of inhibitors of endothiapepsin. Here, we have optimized a hit, identified by de novo structure-based drug design (SBDD) and DCC, by using structure-based design approaches focusing on the optimization of an amide-π interaction. Biochemical results are in agreement with SBDD. These results will provide useful insights for future structure-based optimization of inhibitors for the real drug targets as well as insights into molecular recognition.
Keywords: aspartic protease endothiapepsin; inhibitors; molecular recognition; structure-based drug design.
Figures
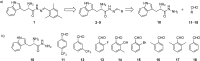
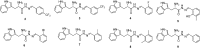
Similar articles
-
Design and Synthesis of Bioisosteres of Acylhydrazones as Stable Inhibitors of the Aspartic Protease Endothiapepsin.ChemMedChem. 2018 Nov 6;13(21):2266-2270. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201800446. Epub 2018 Oct 9. ChemMedChem. 2018. PMID: 30178575 Free PMC article.
-
Fragment Linking and Optimization of Inhibitors of the Aspartic Protease Endothiapepsin: Fragment-Based Drug Design Facilitated by Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016 Aug 1;55(32):9422-6. doi: 10.1002/anie.201603074. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016. PMID: 27400756 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of endothiapepsin complexed with a Phe-Tyr reduced-bond inhibitor at 1.35 Å resolution.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014 Jan;70(Pt 1):30-3. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X13032974. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014. PMID: 24419612 Free PMC article.
-
Aspartic proteases in drug discovery.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(3):271-85. doi: 10.2174/138161207779313560. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17313361 Review.
-
Design of potent aspartic protease inhibitors to treat various diseases.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2008 Sep;341(9):523-35. doi: 10.1002/ardp.200700267. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2008. PMID: 18763714 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-Templated Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry: Brief Overview and Experimental Protocol.European J Org Chem. 2019 Jun 16;2019(22):3581-3590. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201900327. Epub 2019 May 29. European J Org Chem. 2019. PMID: 31680778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH-Dependent Structural Dynamics of Cathepsin D-Family Aspartic Peptidase of Clonorchis sinensis.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 2;10(9):1128. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091128. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34578162 Free PMC article.
-
An in silico approach for identification of novel inhibitors as potential therapeutics targeting COVID-19 main protease.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Aug;39(12):4304-4315. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1776158. Epub 2020 Jun 16. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32544024 Free PMC article.
-
Urea-aromatic interactions in biology.Biophys Rev. 2020 Feb;12(1):65-84. doi: 10.1007/s12551-020-00620-9. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Biophys Rev. 2020. PMID: 32067192 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

