Therapy of Liver Abscesses
- PMID: 26287275
- PMCID: PMC4513824
- DOI: 10.1159/000366579
Therapy of Liver Abscesses
Abstract
Background: Liver abscess (LA) is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening disease with significant morbidity and mortality.
Methods: This review comprehensively describes epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of LA, with a strong focus on antimicrobial treatment choices and the impact of multidrug-resistant pathogens.
Results: In industrialized areas, pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) accounts for over 80% of the cases, whereas Entamoeba histolyticais responsible for up to 10% of the cases, with a higher incidence in tropical areas. Highly virulent strains of Klebsiella pneumoniaehave emerged as a predominant cause of PLA in Asian countries and tend to spread to the USA, Australia, and European countries, therefore requiring special alertness. Most common symptoms of LA are fever, chills, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain, although a broad spectrum of non-specific symptoms may also occur.
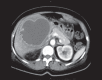
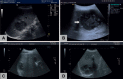
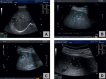
Conclusion: Imaging studies (ultrasound, computed tomography scan) and microbiological findings play a crucial role in the diagnosis of LA. The treatment of choice for PLA is a multimodal approach combining broad-spectrum antibiotics and aspiration or drainage of larger abscess cavities. Amebic LA can be cured by metronidazole therapy without drainage.
Hintergrund: Leberabszesse (LA) sind eine seltene, jedoch potenziell lebensbedrohliche Erkrankung mit relevanter Morbidität und Mortalität.
Methoden: Diese Übersicht beschreibt ausführlich Epidemiologie, Pathogenese, diagnostische Verfahren und Behandlung des LA. Der Schwerpunkt der Arbeit liegt dabei auf der Auswahl der geeigneten antibiotischen Therapie sowie des Managements bei Nachweis multiresistenter Erreger.
Ergebnisse: Eitrige/pyogene Leberabszesse (PLA) sind mit über 80% die häufigste Entität in industrialisierten Gebieten, während Entamoeba histolyticain ca. 10% der Fälle als Erreger identifiziert werden kann. In tropischen Gebieten ist die Inzidenz der Amöben-LA deutlich höher. Hochvirulente Stämme von Klebsiella pneumoniae haben sich in Asien zur Hauptursache der PLA entwickelt. Die zunehmende Verbreitung von K. pneumoniae auch in den USA, in Australien und in europäischen Ländern stellt eine Herausforderung für die Behandlung und Prävention von Sekundärkomplikationen dar. Typische Symptome bei LA sind Fieber, Schüttelfrost und rechtsseitiger Oberbauchschmerz, obgleich eine Vielzahl anderer, unspezifischer Symptome auftreten kann.
Schlussfolgerung: Bildgebung (Ultraschall, Computertomographie) sowie mikrobiologische Untersuchungen sind geeignete diagnostische Verfahren bei klinischem Verdacht auf einen LA. Das multimodale Management des PLA beinhaltet die Therapie mit einem Breitspektrum-Antibiotikum sowie die Aspiration oder Drainage größerer Abszesse. Amöben-LA können durch Metronidazol geheilt werden und benötigen keine Drainage.
Keywords: Amebic liver abscess; Antibiotics; Aspiration; Drainage; Entamoeba histolytica; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Liver abscess; Multidrug-resistant pathogens; Pyogenic liver abscess.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pyogenic and amebic liver abscesses.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004 Aug;6(4):273-9. doi: 10.1007/s11894-004-0078-2. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15245694 Review.
-
Clinical, microbiological, and molecular epidemiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pyogenic liver abscess in southeastern China.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019 Oct 29;8:166. doi: 10.1186/s13756-019-0615-2. eCollection 2019. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019. PMID: 31673355 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic amebiasis.Clin Chest Med. 2002 Jun;23(2):479-92. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(01)00008-9. Clin Chest Med. 2002. PMID: 12092041 Review.
-
Pyogenic liver abscess.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2000;1(1):15-21. doi: 10.1089/109629600321254. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2000. PMID: 12594905
-
A complex presentation of an uncommon disease: Gas-forming pyogenic liver abscess complicated by septic pulmonary emboli and muscle abscesses, a case report and review of the literature.IDCases. 2022 Dec 22;31:e01673. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01673. eCollection 2023. IDCases. 2022. PMID: 36632483 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of a conservative approach to management in amoebic liver abscess.J Postgrad Med. 2017 Jan-Mar;63(1):16-20. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.191004. J Postgrad Med. 2017. PMID: 27652983 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet Transmission of Streptococcus sanguinis Causing Pyogenic Liver Abscess in a Male Patient With a Transplanted Liver.Cureus. 2024 Oct 10;16(10):e71228. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71228. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39525212 Free PMC article.
-
Complicated Isolated Liver Abscess Caused by Viridans Group Streptococci Leading to Right Hepatectomy.Cureus. 2020 Jul 12;12(7):e9149. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9149. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32789086 Free PMC article.
-
Klebsiella Pneumoniae Liver Abscess: A Case Series of Six Asian Patients.Am J Case Rep. 2017 Sep 26;18:1028-1033. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.905191. Am J Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28947732 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus constellatus: a rare causative agent of pyogenic liver abscess.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Dec 18;12(12):e229738. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229738. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31857289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, Holzman RS. Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1654–1659. - PubMed
-
- Wong WM, Wong BC, Hui CK, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess: retrospective analysis of 80 cases over a 10-year study period. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:1001–1007. - PubMed
-
- Siu LK, Yeh KM, Lin JC, et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: a new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:881–887. - PubMed
-
- Chung DR, Lee SS, Lee HR, et al. the Korean Study Group for Liver Abscess Emerging invasive liver abscess caused by K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniaein Korea. J Infect. 2007;54:578–583. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

