Obstructions to Sampling Qualitative Properties
- PMID: 26287384
- PMCID: PMC4546154
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135636
Obstructions to Sampling Qualitative Properties
Abstract
Background: Sampling methods have proven to be a very efficient and intuitive method to understand properties of complicated spaces that cannot easily be computed using deterministic methods. Therefore, sampling methods became a popular tool in the applied sciences.
Results: Here, we show that sampling methods are not an appropriate tool to analyze qualitative properties of complicated spaces unless RP = NP. We illustrate these results on the example of the thermodynamically feasible flux space of genome-scale metabolic networks and show that with artificial centering hit and run (ACHR) not all reactions that can have variable flux rates are sampled with variables flux rates. In particular a uniform sample of the flux space would not sample the flux variabilities completely.
Conclusion: We conclude that unless theoretical convergence results exist, qualitative results obtained from sampling methods should be considered with caution and if possible double checked using a deterministic method.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
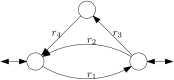

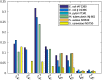
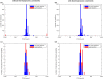
Similar articles
-
ll-ACHRB: a scalable algorithm for sampling the feasible solution space of metabolic networks.Bioinformatics. 2016 Aug 1;32(15):2330-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw132. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27153696
-
optGpSampler: an improved tool for uniformly sampling the solution-space of genome-scale metabolic networks.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 14;9(2):e86587. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086587. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24551039 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of Monte Carlo sampling methods for metabolic network models.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 1;15(7):e0235393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235393. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32609776 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting structural invariants in biological reaction networks.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;804:377-407. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-361-5_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22144164 Review.
-
Flux analysis and metabolomics for systematic metabolic engineering of microorganisms.Biotechnol Adv. 2013 Nov;31(6):818-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 13. Biotechnol Adv. 2013. PMID: 23680193 Review.
Cited by
-
Estimating Metabolic Fluxes Using a Maximum Network Flexibility Paradigm.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 12;10(10):e0139665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139665. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26457579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lovász L. Hit-and-run mixes fast. Mathematical Programming. 1999;86(3):443–461.
-
- Dyer M, Frieze A, Kannan R. A random polynomial-time algorithm for approximating the volume of convex bodies. Journal of the ACM. 1991;38(1):1–17. 10.1145/102782.102783 - DOI
-
- Lovász L, Vempala S. Simulated annealing in convex bodies and an O*(n 4) volume algorithm. Journal of Computer and System Sciences. 2006;72(2):392–417. 10.1016/j.jcss.2005.08.004 - DOI
-
- Elekes G. A geometric inequality and the complexity of computing volume. Discrete and Computational Geometry. 1986;1(1):289–292. 10.1007/BF02187701 - DOI
-
- Bárány I, Füredi Z. Computing the volume is difficult. Discrete and Computational Geometry. 1987;2(1):319–326. 10.1007/BF02187886 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

