Repigmentation of Hypopigmented Scars Using Combination of Fractionated Carbon Dioxide Laser with Topical Latanoprost Vs. Fractionated Carbon Dioxide Laser Alone
- PMID: 26288404
- PMCID: PMC4533534
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.160481
Repigmentation of Hypopigmented Scars Using Combination of Fractionated Carbon Dioxide Laser with Topical Latanoprost Vs. Fractionated Carbon Dioxide Laser Alone
Abstract
Background: Fractionated carbon dioxide (CO2) can treat hypopigmented scars. Latanoprost is a prostaglandin analog used to treat glaucoma. It can cause adverse effects, such as periocular hyperpigmentation. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of latanoprost plus CO2 laser on the repigmentation of hypopigmented scars.
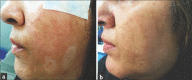
Patients and methods: 28 patients with hypopigmented scars were divided randomly into two groups. The patients in group A were treated in six sessions (1-month intervals) with 10600-nm fractional CO2 laser plus latanoprost 0.005% and those of group B fractionated CO2 laser plus placebo (distilled water). Digital photographs were taken at baseline and 3 months after the last treatment session. The blinded dermatologist compared the photographs and evaluated the efficacy of treatment in the hypopigmented scars using a 4-scale point (grade 1-4). Patient satisfaction was scored from 0 to 10 on a visual analog scale.
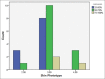
Results: Follow-up results 12 weeks after the last treatment session demonstrated that 11 of the 14 patients in group A had more than 50% improvement in hypopigmentation The difference in improvement of the two groups was statistically significant (P = 0.027). The mean of the VAS scores of patients in group A was 6.50 ± 1.45 and in group B 4.57 ± 1.6. The difference in mean satisfaction of the two groups was statistically significant (P = 0.003). Side effects were mild and resolved within 1 to 5 days.
Conclusion: The fractional CO2 laser resurfacing plus topical latanoprost can be used as a safe and efficacious method to treat hypopigmented scars.
Keywords: Fractionated carbon dioxide laser; fractionated carbon dioxide laser; hypopigmented scars; latanoprost.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Massaki AB, Fabi SG, Fitzpatrick R. Repigmentation of hypopigmented scars using an erbium-doped 1,550-nm fractionated laser and topical bimatoprost. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:995–1001. - PubMed
-
- Alexiades-Armenakas MR, Bernstein LJ, Friedman PM, Geronemus RG. The safety and efficacy of the 308-nm excimer laser for pigment correction of hypopigmented scars and striae alba. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:955–60. - PubMed
-
- Alster T, Zaulyanov L. Laser scar revision: A review. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:131–40. - PubMed
-
- Kauvar A, Hruza G. Miami, FL, U.S.A: Informa Health Care; 2005. Principles and Practices in Cutaneous Laser Surgery; pp. 841–8.
-
- Manstein D, Herron GS, Sink RK, Tanner H, Anderson RR. Fractional photothermolysis: A new concept for cutaneous remodeling using microscopic patterns of thermal injury. Lasers Surg Med. 2004;34:426–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
