Expedited quantification of mutant ribosomal RNA by binary deoxyribozyme (BiDz) sensors
- PMID: 26289345
- PMCID: PMC4574759
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.052613.115
Expedited quantification of mutant ribosomal RNA by binary deoxyribozyme (BiDz) sensors
Abstract
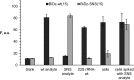
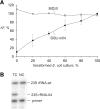
Mutations in ribosomal RNA (rRNA) have traditionally been detected by the primer extension assay, which is a tedious and multistage procedure. Here, we describe a simple and straightforward fluorescence assay based on binary deoxyribozyme (BiDz) sensors. The assay uses two short DNA oligonucleotides that hybridize specifically to adjacent fragments of rRNA, one of which contains a mutation site. This hybridization results in the formation of a deoxyribozyme catalytic core that produces the fluorescent signal and amplifies it due to multiple rounds of catalytic action. This assay enables us to expedite semi-quantification of mutant rRNA content in cell cultures starting from whole cells, which provides information useful for optimization of culture preparation prior to ribosome isolation. The method requires less than a microliter of a standard Escherichia coli cell culture and decreases analysis time from several days (for primer extension assay) to 1.5 h with hands-on time of ∼10 min. It is sensitive to single-nucleotide mutations. The new assay simplifies the preliminary analysis of RNA samples and cells in molecular biology and cloning experiments and is promising in other applications where fast detection/quantification of specific RNA is required.
Keywords: binary deoxyribozyme; fluorescent sensors; mix-and-read probes; mutation analysis; ribosomal RNA.
© 2015 Gerasimova et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures

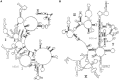



Similar articles
-
Photolabile oligoDNA probes of internal Escherichia coli ribosomal structure.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995;(33):59-62. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995. PMID: 8643399
-
Conserved portion in bacterial ribosomal RNA.J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2004 Dec;50(6):363-70. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15965891
-
Sequence-specific cleavage of small-subunit (SSU) rRNA with oligonucleotides and RNase H: a rapid and simple approach to SSU rRNA-based quantitative detection of microorganisms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jun;70(6):3650-63. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3650-3663.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184170 Free PMC article.
-
What do we know about ribosomal RNA methylation in Escherichia coli?Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25511423 Review.
-
[Study of ribosome structure using the biochemical methods: judgment day].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001 Jul-Aug;35(4):559-83. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001. PMID: 11524944 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Cascade of deoxyribozymes for the colorimetric analysis of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Oct 1;165:112385. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112385. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32729510 Free PMC article.
-
Divide and Control: Comparison of Split and Switch Hybridization Sensors.ChemistrySelect. 2017 Jul 3;2(19):5427-5431. doi: 10.1002/slct.201701179. Epub 2017 Jul 4. ChemistrySelect. 2017. PMID: 29372178 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Nanomachine (DNM) Biplex Assay for Differentiating Bacillus cereus Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 24;24(5):4473. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054473. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901903 Free PMC article.
-
Label-Free Pathogen Detection by a Deoxyribozyme Cascade with Visual Signal Readout.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019 Mar 1;282:945-951. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.147. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019. PMID: 31462856 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Antenna Tile-Associated Deoxyribozyme Sensor with Improved Sensitivity.Chembiochem. 2016 Nov 3;17(21):2038-2041. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201600438. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Chembiochem. 2016. PMID: 27620365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burakovsky DE, Sergiev PV, Steblyanko MA, Konevega AL, Bogdanov AA, Dontsova OA. 2011. The structure of helix 89 of 23S rRNA is important for peptidyl transferase function of Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett 585: 3073–3078. - PubMed
-
- Cox RA. 2003. Correlation of the rate of protein synthesis and the third power of the RNA: protein ratio in Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbiology 149: 729–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
