Spatiotemporal profiles of receptive fields of neurons in the lateral posterior nucleus of the cat LP-pulvinar complex
- PMID: 26289469
- PMCID: PMC4620137
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00649.2015
Spatiotemporal profiles of receptive fields of neurons in the lateral posterior nucleus of the cat LP-pulvinar complex
Abstract
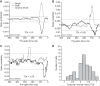
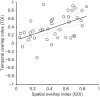
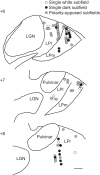
The pulvinar is the largest extrageniculate thalamic visual nucleus in mammals. It establishes reciprocal connections with virtually all visual cortexes and likely plays a role in transthalamic cortico-cortical communication. In cats, the lateral posterior nucleus (LP) of the LP-pulvinar complex can be subdivided in two subregions, the lateral (LPl) and medial (LPm) parts, which receive a predominant input from the striate cortex and the superior colliculus, respectively. Here, we revisit the receptive field structure of LPl and LPm cells in anesthetized cats by determining their first-order spatiotemporal profiles through reverse correlation analysis following sparse noise stimulation. Our data reveal the existence of previously unidentified receptive field profiles in the LP nucleus both in space and time domains. While some cells responded to only one stimulus polarity, the majority of neurons had receptive fields comprised of bright and dark responsive subfields. For these neurons, dark subfields' size was larger than that of bright subfields. A variety of receptive field spatial organization types were identified, ranging from totally overlapped to segregated bright and dark subfields. In the time domain, a large spectrum of activity overlap was found, from cells with temporally coinciding subfield activity to neurons with distinct, time-dissociated subfield peak activity windows. We also found LP neurons with space-time inseparable receptive fields and neurons with multiple activity periods. Finally, a substantial degree of homology was found between LPl and LPm first-order receptive field spatiotemporal profiles, suggesting a high integration of cortical and subcortical inputs within the LP-pulvinar complex.
Keywords: cortico-thalamo-cortical pathways; electrophysiology; reverse correlation; thalamus; visual system.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures








References
-
- Abramson BP, Chalupa LM. The laminar distribution of cortical connections with the tecto- and cortico-recipient zones in the cat's lateral posterior nucleus. Neuroscience 15: 81–95, 1985. - PubMed
-
- Bender DB. Receptive-field properties of neurons in the macaque inferior pulvinar. J Neurophysiol 48: 1–17, 1982. - PubMed
-
- Bender DB. Visual activation of neurons in the primate pulvinar depends on cortex but not colliculus. Brain Res 279: 258–261, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Berson DM, Graybiel AM. Organization of the striate-recipient zone of the cats lateralis posterior-pulvinar complex and its relations with the geniculostriate system. Neuroscience 9: 337–372, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Boire D, Matteau I, Casanova C, Ptito M. Retinal projections to the lateral posterior-pulvinar complex in intact and early visual cortex lesioned cats. Exp Brain Res 159: 185–196, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

