Heparan sulfate and heparin interactions with proteins
- PMID: 26289657
- PMCID: PMC4614469
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2015.0589
Heparan sulfate and heparin interactions with proteins
Abstract
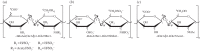
Heparan sulfate (HS) polysaccharides are ubiquitous components of the cell surface and extracellular matrix of all multicellular animals, whereas heparin is present within mast cells and can be viewed as a more sulfated, tissue-specific, HS variant. HS and heparin regulate biological processes through interactions with a large repertoire of proteins. Owing to these interactions and diverse effects observed during in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo experiments, manifold biological/pharmacological activities have been attributed to them. The properties that have been thought to bestow protein binding and biological activity upon HS and heparin vary from high levels of sequence specificity to a dependence on charge. In contrast to these opposing opinions, we will argue that the evidence supports both a level of redundancy and a degree of selectivity in the structure-activity relationship. The relationship between this apparent redundancy, the multi-dentate nature of heparin and HS polysaccharide chains, their involvement in protein networks and the multiple binding sites on proteins, each possessing different properties, will also be considered. Finally, the role of cations in modulating HS/heparin activity will be reviewed and some of the implications for structure-activity relationships and regulation will be discussed.
Keywords: cations; heparan sulfate; heparin; polysaccharide; protein binding; redundancy.
© 2015 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Perlin AS, Mackie DM, Dietrich CP. 1971. Evidence for a (1→4)-linked 4-O-(-l-idopyranosyluronic acid 2-sulfate)-(2-deoxy-2-sulfoamino-d-glucopyranosyl 6-sulfate) sequence in heparin. Long-range H-H coupling in 4-deoxy-hex-4-enopyranosides. Carbohydr. Res. 18, 185–194. (10.1016/S0008-6215(00)80341-9) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Casu B, et al. 1996. Characterization of sulfation patterns of beef and pig mucosal heparins by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arzneimittelforschung 46, 472–477. - PubMed
-
- Bianchini P, Osima B, Parma B, Nader HB, Dietrich CP. 1985. Lack of correlation between ‘in vitro’ and ‘in vivo’ antithrombotic activity of heparin fractions and related compounds. Heparan sulfate as an antithrombotic agent ‘in vivo’. Thromb. Res. 40, 597–607. (10.1016/0049-3848(85)90298-1) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dietrich CP, et al. 1998. Structure of heparan sulfate: identification of variable and constant oligosaccharide domains in eight heparan sulfates of different origins. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand). 44, 417–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

