Selection in the dopamine receptor 2 gene: a candidate SNP study
- PMID: 26290802
- PMCID: PMC4540012
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1149
Selection in the dopamine receptor 2 gene: a candidate SNP study
Abstract
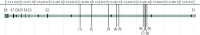
Dopamine is a major neurotransmitter in the human brain and is associated with various diseases. Schizophrenia, for example, is treated by blocking the dopamine receptors type 2. Shaner, Miller & Mintz (2004) stated that schizophrenia was the low fitness variant of a highly variable mental trait. We therefore explore whether the dopamine receptor 2 gene (DRD2) underwent any selection processes. We acquired genotype data of the 1,000 Genomes project (phase I), which contains 1,093 individuals from 14 populations. We included single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with two minor allele frequencies (MAFs) in the analysis: MAF over 0.05 and over 0.01. This is equivalent to 151 SNPs (MAF > 0.05) and 246 SNPs (MAF > 0.01) for DRD2. We used two different approaches (an outlier approach and a Bayesian approach) to detect loci under selection. The combined results of both approaches yielded nine (MAF > 0.05) and two candidate SNPs (MAF > 0.01), under balancing selection. We also found weak signs for directional selection on DRD2, but in our opinion these were too weak to draw any final conclusions on directional selection in DRD2. All candidates for balancing selection are in the intronic region of the gene and only one (rs12574471) has been mentioned in the literature. Two of our candidate SNPs are located in specific regions of the gene: rs80215768 lies within a promoter flanking region and rs74751335 lies within a transcription factor binding site. We strongly encourage research on our candidate SNPs and their possible effects.
Keywords: DRD2; Dopamine; Dopamine receptor 2; Schizophrenia; Selection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Association of D2 Dopamine Receptor Gene and Reported Allele Frequencies With Alcohol Use Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Nov 1;2(11):e1914940. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.14940. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31702801 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of QTL minor allele frequency on genomic evaluation using real genotype data and simulated phenotypes in Japanese Black cattle.BMC Genet. 2015 Nov 19;16:134. doi: 10.1186/s12863-015-0287-8. BMC Genet. 2015. PMID: 26586567 Free PMC article.
-
Association study of dopamine transporter gene and schizophrenia in Korean population using multiple single nucleotide polymorphism markers.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;28(6):975-83. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2004.05.015. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15380858
-
Association of Dopamine D2 Receptor Gene Polymorphisms with Reproduction Traits in Domestic Pigeons (Columba livia).J Poult Sci. 2017 Jan 25;54(1):13-17. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0160037. J Poult Sci. 2017. PMID: 32908403 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating outlier loci and their effect on the identification of pedigree errors.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S155. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S155. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451616 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Signatures of Natural Selection for Polymorphic Genes of the Human Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Systems: A Review.Front Psychol. 2016 Jun 8;7:857. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00857. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27375535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

