Rare variant discovery by deep whole-genome sequencing of 1,070 Japanese individuals
- PMID: 26292667
- PMCID: PMC4560751
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9018
Rare variant discovery by deep whole-genome sequencing of 1,070 Japanese individuals
Abstract
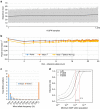
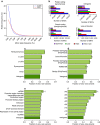
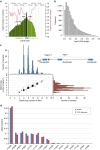
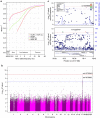
The Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization reports the whole-genome sequences of 1,070 healthy Japanese individuals and construction of a Japanese population reference panel (1KJPN). Here we identify through this high-coverage sequencing (32.4 × on average), 21.2 million, including 12 million novel, single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) at an estimated false discovery rate of <1.0%. This detailed analysis detected signatures for purifying selection on regulatory elements as well as coding regions. We also catalogue structural variants, including 3.4 million insertions and deletions, and 25,923 genic copy-number variants. The 1KJPN was effective for imputing genotypes of the Japanese population genome wide. These data demonstrate the value of high-coverage sequencing for constructing population-specific variant panels, which covers 99.0% SNVs of minor allele frequency ≥0.1%, and its value for identifying causal rare variants of complex human disease phenotypes in genetic association studies.
Figures
References
-
- Lander E. S. et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Ozaki K. et al. Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-alpha gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 32, 650–654 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Reich D. E. & Lander E. S. On the allelic spectrum of human disease. Trends Genet. 17, 502–510 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

