The Architecture of the TIR Domain Signalosome in the Toll-like Receptor-4 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 26293885
- PMCID: PMC4544004
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13128
The Architecture of the TIR Domain Signalosome in the Toll-like Receptor-4 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
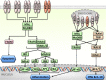
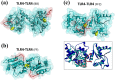
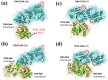
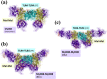
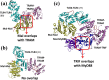
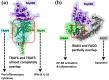
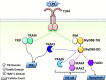
Activated Toll-like receptors (TLRs) cluster in lipid rafts and induce pro- and anti-tumor responses. The organization of the assembly is critical to the understanding of how these key receptors control major signaling pathways in the cell. Although several models for individual interactions were proposed, the entire TIR-domain signalosome architecture has not been worked out, possibly due to its complexity. We employ a powerful algorithm, crystal structures and experimental data to model the TLR4 and its cluster. The architecture that we obtain with 8 MyD88 molecules provides the structural basis for the MyD88-templated myddosome helical assembly and receptor clustering; it also provides clues to pro- and anti-inflammatory signaling pathways branching at the signalosome level to Mal/MyD88 and TRAM/TRIF pro- and anti-inflammatory pathways. The assembly of MyD88 death domain (DD) with TRAF3 (anti-viral/anti-inflammatory) and TRAF6 (pro-inflammatory) suggest that TRAF3/TRAF6 binding sites on MyD88 DD partially overlap, as do IRAK4 and FADD. Significantly, the organization illuminates mechanisms of oncogenic mutations, demonstrates that almost all TLR4 parallel pathways are competitive and clarifies decisions at pathway branching points. The architectures are compatible with the currently-available experimental data and provide compelling insights into signaling in cancer and inflammation pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In silico approach to inhibition of signaling pathways of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 by ST2L.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023989. Epub 2011 Aug 29. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21897866 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the multiple interactions of the MyD88 TIR domain in TLR4 signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 23;106(25):10260-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812956106. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19506249 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of binding sites for myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88) and Toll-like receptor 4 in MyD88 adapter-like (Mal).J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):12054-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.415810. Epub 2013 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23460645 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor mediated signaling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Apr;83(4):258-66. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0622-4. Epub 2005 Jan 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15662540 Review.
-
Microbial recognition by Toll-like receptors.J Dermatol Sci. 2004 Apr;34(2):73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2003.10.002. J Dermatol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15033189 Review.
Cited by
-
Polarization of Low-Grade Inflammatory Monocytes Through TRAM-Mediated Up-Regulation of Keap1 by Super-Low Dose Endotoxin.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 16;11:1478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01478. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32765513 Free PMC article.
-
Negative Regulation of TLR Signaling by BCAP Requires Dimerization of Its DBB Domain.J Immunol. 2020 Apr 15;204(8):2269-2276. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901210. Epub 2020 Mar 20. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32198144 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF3/CYLD mutations identify a distinct subset of human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer. 2017 May 15;123(10):1778-1790. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30570. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28295222 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in different interactions between toll-like receptors and hepatitis B infection: a review.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 13;15:1363996. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1363996. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38545106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of Protein Interactions by Structural Matching: Prediction of PPI Networks and the Effects of Mutations on PPIs that Combines Sequence and Structural Information.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1558:255-270. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6783-4_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28150242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guven Maiorov E., Keskin O., Gursoy A. & Nussinov R. The structural network of inflammation and cancer: merits and challenges. Semin Cancer Biol 23, 243–51 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G. Cancer and inflammation: an old intuition with rapidly evolving new concepts. Annu Rev Immunol 30, 677–706 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Rakoff-Nahoum S. & Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9, 57–63 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

