Atypical role of sprouty in p21 dependent inhibition of cell proliferation in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 26293890
- PMCID: PMC4873464
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.22379
Atypical role of sprouty in p21 dependent inhibition of cell proliferation in colorectal cancer
Abstract
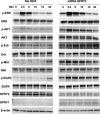
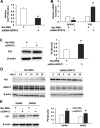
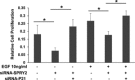
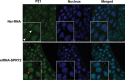
Sprouty (SPRY) appears to act as a tumor suppressor in cancer, whereas we reported that SPRY2 functions as a putative oncogene in colorectal cancer (CRC) [Oncogene, 2010, 29: 5241-5253]. In general, various studies established inhibition of cell proliferation by SPRY in cancer. The mechanisms by which SPRY regulates cell proliferation in CRC are investigated. We demonstrate, for the first time, suppression of SPRY2 augmented EGF-dependent oncogenic signaling, however, surprisingly decreased cell proliferation in colon cancer cells. Our data suggest that cell cycle inhibitor p21(WAF1/CIP1) transcriptional activity being regulated by SPRY2. Indeed, suppression of SPRY2 significantly increased p21(WAF1/CIP1) mRNA and protein expression as well as p21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter activity. Conversely, overexpressing SPRY2 triggered a decrease in p21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter activity. Concurrent down-regulation of both SPRY1 and SPRY2 also increased p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression in colon cancer cells. Increased nuclear localization of p21(WAF1/CIP1) in SPRY2 downregulated colon cancer cells may explain the inhibition of cell proliferation in colon cancer cells. Underscoring the biological relevance of these findings in SPRY1 and SPRY2 mutant mouse, recombination of floxed SPRY1 and SPRY2 alleles in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) resulted in increased expression and nuclear localization of p21(WAF1/CIP1) and decreased cell proliferation. In CRC, the relationship of SPRY with p21 may provide unique strategies for cancer prevention and treatment. © 2015 The Authors. Molecular Carcinogenesis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: MEF; cancer; colon; mouse; p21; sprouty.
© 2015 The Authors. Molecular Carcinogenesis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Atypical role of sprouty in colorectal cancer: sprouty repression inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 16;35(24):3151-62. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.365. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26434583 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglioside GM3 modulates tumor suppressor PTEN-mediated cell cycle progression--transcriptional induction of p21(WAF1) and p27(kip1) by inhibition of PI-3K/AKT pathway.Glycobiology. 2006 Jul;16(7):573-83. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwj105. Epub 2006 Mar 30. Glycobiology. 2006. PMID: 16574813
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated proliferation of enterocytes requires p21waf1/cip1 expression.Gastroenterology. 2006 Jul;131(1):153-64. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.05.007. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16831599
-
p21Waf1/Cip1: its paradoxical effect in the regulation of breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2019 Mar;26(2):131-137. doi: 10.1007/s12282-018-0913-1. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Breast Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30255294 Review.
-
Examination of the expanding pathways for the regulation of p21 expression and activity.Cell Signal. 2010 Jul;22(7):1003-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.013. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20100570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sprouty2 enhances the tumorigenic potential of glioblastoma cells.Neuro Oncol. 2018 Jul 5;20(8):1044-1054. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noy028. Neuro Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29635363 Free PMC article.
-
The pseudogene derived from long non-coding RNA DUXAP10 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through epigenetically silencing of p21 and PTEN.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 4;7(1):7312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07954-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28779166 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of SPRY2 in human hepatocytes leads to increased glucose uptake and lipid droplet accumulation.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Oct 29;19(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0442-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 31664995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hacohen N, Kramer S, Sutherland D, et al. Sprouty encodes a novel antagonist of fgf signaling that patterns apical branching of the drosophila airways. Cell 1998; 92:253–263. - PubMed
-
- Leeksma OC, Van Achterberg TA, Tsumura Y, et al. Human sprouty 4, a new Ras antagonist on 5q31, interacts with the dual specificity kinase tesk1. Eur J Biochem 2002; 269:2546–2556. - PubMed
-
- Gross I, Bassit B, Benezra M, et al. Mammalian sprouty proteins inhibit cell growth and differentiation by preventing ras activation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:46460–46468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

