Lipoma of the Small Intestine: A Cause for Intussusception in Adults
- PMID: 26295002
- PMCID: PMC4532934
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/856030
Lipoma of the Small Intestine: A Cause for Intussusception in Adults
Abstract
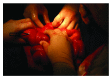
Intussusception as a cause of intestinal obstruction in adults is rare. There is invariably an underlying pathology which leads to intussusception in adults. A case of intussusception in an adult due to a small intestinal lipoma is presented in view of this association. Ultrasound and CECT may help in a preoperative diagnosis. However early surgical intervention is the mainstay of treatment in order to confirm the diagnosis of the underlying pathology, thereby avoiding misdiagnosis of an underlying cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Akcay M. N., Polat M., Cadirci M., Gencer B. Tumor-induced ileo-ileal invagination in adults. American Surgeon. 1994;60(12):980–981. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

