Terpenoids from the Octocoral Sinularia gaweli
- PMID: 26295226
- PMCID: PMC4581310
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160819508
Terpenoids from the Octocoral Sinularia gaweli
Abstract
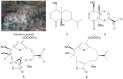
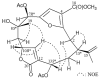
Two eudesmane sesquiterpenoids, verticillatol (1) and 5α-acetoxy-4(14)-eudesmene-1β-ol (2) and two cembrane diterpenoids, (-)-leptodiol acetate (3) and sinulacembranolide A (4) were isolated from the octocoral Sinularia gaweli and compounds 2-4 are new isolates. The structures of new terpenoids 2-4 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and by comparison the spectral data with those of known analogues. Terpenoid 4 was found to inhibit the accumulation of the pro-inflammatory inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 marcophage cells.
Keywords: Sinularia gaweli; cembrane; eudesmane; iNOS; octocoral.
Figures


References
-
- Chen W.-T., Li Y., Guo Y.-W. Terpenoids of Sinularia soft corals: Chemistry and bioactivity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2012;2:227–237. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2012.04.004. - DOI
-
- Yen W.-H., Su Y.-D., Chang Y.-C., Chen Y.-H., Chen Y.-H., Dai C.-F., Wen Z.-H., Su J.-H., Sung P.-J. Sinulanorcembranolide A, a novel norcembranoidal diterpene from the octocoral Sinularia gaweli. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013;54:2267–2270. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2013.02.077. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

