The Matchmaker Exchange: a platform for rare disease gene discovery
- PMID: 26295439
- PMCID: PMC4610002
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.22858
The Matchmaker Exchange: a platform for rare disease gene discovery
Abstract
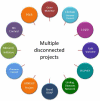
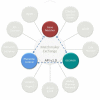
There are few better examples of the need for data sharing than in the rare disease community, where patients, physicians, and researchers must search for "the needle in a haystack" to uncover rare, novel causes of disease within the genome. Impeding the pace of discovery has been the existence of many small siloed datasets within individual research or clinical laboratory databases and/or disease-specific organizations, hoping for serendipitous occasions when two distant investigators happen to learn they have a rare phenotype in common and can "match" these cases to build evidence for causality. However, serendipity has never proven to be a reliable or scalable approach in science. As such, the Matchmaker Exchange (MME) was launched to provide a robust and systematic approach to rare disease gene discovery through the creation of a federated network connecting databases of genotypes and rare phenotypes using a common application programming interface (API). The core building blocks of the MME have been defined and assembled. Three MME services have now been connected through the API and are available for community use. Additional databases that support internal matching are anticipated to join the MME network as it continues to grow.
Keywords: GA4GH, IRDiRC; Matchmaker Exchange; gene discovery; genomic API; matchmaking; rare disease.
© 2015 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Figures
References
-
- Au PYB, You J, Caluseriu O, Schwartzentruber J, Majewski J, Bernier FP, Ferguson M, Care for Rare Canada Consortium. Valle D, Parboosingh JS, Sobreira S, Innes AM, Kline AD. GeneMatcher aids in the identification of a new malformation syndrome with intellectual disability, unique facial dysmorphisms, and skeletal and connective tissue caused by de novo variants in HNRNPK. Hum Mutat. 2015;36 xxx-yyy. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG007690/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG006834/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG007990/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG007530/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R24OD011883/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HD077671/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 OD011883/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007530/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- EP1-120608/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U41HG006834/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01CO42400-80/CO/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS065712/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EP2-120609/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U54HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HD077671/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HG007690/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54NS065712/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007748/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG007990/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 5R01NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007748/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

