Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay
- PMID: 26296072
- PMCID: PMC4556774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.010
Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay
Abstract
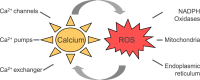
Calcium is an important second messenger involved in intra- and extracellular signaling cascades and plays an essential role in cell life and death decisions. The Ca(2+) signaling network works in many different ways to regulate cellular processes that function over a wide dynamic range due to the action of buffers, pumps and exchangers on the plasma membrane as well as in internal stores. Calcium signaling pathways interact with other cellular signaling systems such as reactive oxygen species (ROS). Although initially considered to be potentially detrimental byproducts of aerobic metabolism, it is now clear that ROS generated in sub-toxic levels by different intracellular systems act as signaling molecules involved in various cellular processes including growth and cell death. Increasing evidence suggests a mutual interplay between calcium and ROS signaling systems which seems to have important implications for fine tuning cellular signaling networks. However, dysfunction in either of the systems might affect the other system thus potentiating harmful effects which might contribute to the pathogenesis of various disorders.
Keywords: Calcium; Channels; Endoplasmic reticulum; Mitochondria; NADPH oxidases; Reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Antony S., Wu Y., Hewitt S.M., Anver M.R., Butcher D., Jiang G., Meitzler J.L., Liu H., Juhasz A., Lu J., Roy K.K., Doroshow J.H. Characterization of NADPH oxidase 5 expression in human tumors and tumor cell lines with a novel mouse monoclonal antibody. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013;65:497–508. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aon M.A., Cortassa S., Marbán E., O’Rourke B. Synchronized whole cell oscillations in mitochondrial metabolism triggered by a local release of reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:44735–44744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

