Centriolar satellites assemble centrosomal microcephaly proteins to recruit CDK2 and promote centriole duplication
- PMID: 26297806
- PMCID: PMC4574112
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.07519
Centriolar satellites assemble centrosomal microcephaly proteins to recruit CDK2 and promote centriole duplication
Abstract
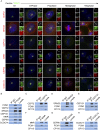
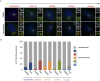
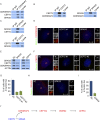
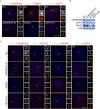
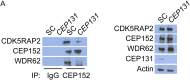
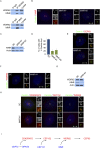
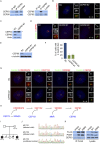
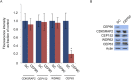
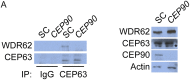
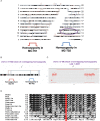
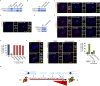
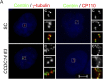
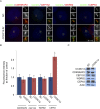
Primary microcephaly (MCPH) associated proteins CDK5RAP2, CEP152, WDR62 and CEP63 colocalize at the centrosome. We found that they interact to promote centriole duplication and form a hierarchy in which each is required to localize another to the centrosome, with CDK5RAP2 at the apex, and CEP152, WDR62 and CEP63 at sequentially lower positions. MCPH proteins interact with distinct centriolar satellite proteins; CDK5RAP2 interacts with SPAG5 and CEP72, CEP152 with CEP131, WDR62 with MOONRAKER, and CEP63 with CEP90 and CCDC14. These satellite proteins localize their cognate MCPH interactors to centrosomes and also promote centriole duplication. Consistent with a role for satellites in microcephaly, homozygous mutations in one satellite gene, CEP90, may cause MCPH. The satellite proteins, with the exception of CCDC14, and MCPH proteins promote centriole duplication by recruiting CDK2 to the centrosome. Thus, centriolar satellites build a MCPH complex critical for human neurodevelopment that promotes CDK2 centrosomal localization and centriole duplication.
Keywords: brain development; cell biology; cell cycle; centriolar satellite; centriole; centrosome; developmental biology; human; microcephaly; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures











References
-
- Andersen JS, Wilkinson CJ, Mayor T, Mortensen P, Nigg EA, Mann M. Proteomic characterization of the human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nature. 2003;426:570–574. - PubMed
-
- Bond J, Roberts E, Springell K, Lizarraga SB, Scott S, Higgins J, Hampshire DJ, Morrison EE, Leal GF, Silva EO, Costa SM, Baralle D, Raponi M, Karbani G, Rashid Y, Jafri H, Bennett C, Corry P, Walsh CA, Woods CG. A centrosomal mechanism involving CDK5RAP2 and CENPJ controls brain size. Nature Genetics. 2005;37:353–355. doi: 10.1038/ng1539. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32HL007731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM095941/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM081879/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR054396/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS035129/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054396/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- Y 597/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
- R01 GM095941/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL089707/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

