Discovery, synthesis and biochemical profiling of purine-2,6-dione derivatives as inhibitors of the human poly(A)-selective ribonuclease Caf1
- PMID: 26299350
- PMCID: PMC4577731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.095
Discovery, synthesis and biochemical profiling of purine-2,6-dione derivatives as inhibitors of the human poly(A)-selective ribonuclease Caf1
Abstract
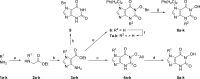
Eukaryotic mRNA contains a 3' poly(A) tail, which plays important roles in the regulation of mRNA stability and translation. Well-characterized enzymes involved in the shortening of the poly(A) tail include the multi-subunit Ccr4-Not deadenylase, which contains the Caf1 (Pop2) and Ccr4 catalytic components, and poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN). Two Mg(2+) ions present in the active sites of these ribonucleases are required for RNA cleavage. Here, we report the discovery, synthesis and biochemical profiling of purine-2,6-dione derivatives as (sub)micromolar inhibitors of Caf1.
Keywords: Caf1/CNOT7; Deadenylase; Mg(2+) dependent nuclease; PARN; Ribonuclease.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

