Accurate Non-parametric Estimation of Recent Effective Population Size from Segments of Identity by Descent
- PMID: 26299365
- PMCID: PMC4564943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.07.012
Accurate Non-parametric Estimation of Recent Effective Population Size from Segments of Identity by Descent
Abstract
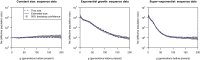
Existing methods for estimating historical effective population size from genetic data have been unable to accurately estimate effective population size during the most recent past. We present a non-parametric method for accurately estimating recent effective population size by using inferred long segments of identity by descent (IBD). We found that inferred segments of IBD contain information about effective population size from around 4 generations to around 50 generations ago for SNP array data and to over 200 generations ago for sequence data. In human populations that we examined, the estimates of effective size were approximately one-third of the census size. We estimate the effective population size of European-ancestry individuals in the UK four generations ago to be eight million and the effective population size of Finland four generations ago to be 0.7 million. Our method is implemented in the open-source IBDNe software package.
Copyright © 2015 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HG004960/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG005701/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- GM099568/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM099568/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HG004960/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 102215/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT091310/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 085475/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GM075091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG005701/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM075091/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

