Synergistic immunotherapeutic effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and interferon-α2b on the murine Renca renal cell carcinoma cell line in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 26300071
- PMCID: PMC4626139
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4230
Synergistic immunotherapeutic effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and interferon-α2b on the murine Renca renal cell carcinoma cell line in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
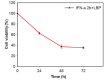
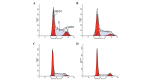
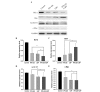
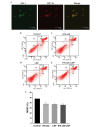
Novel therapeutic strategies to improve clinical efficacy in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are required. The possibility of combination therapy with Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP) and recombinant interferon (IFN)‑α2b remains to be elucidated in RCC. The present study investigated the putative synergistic immunotherapeutic roles of LBP and IFN‑α2b against RCC in vitro and in vivo. The mouse RCC cell line, Renca, was used for in vitro experiments. Treatment of the cells with a combination of LBP and IFN‑α2b markedly inhibited cell proliferation, retarded cell cycle growth and promoted apoptosis in the Renca cells. Western blot analysis revealed that LBP and IFN‑α2b synergistically downregulated the expression levels of cyclin D1, c‑Myc and Bcl‑2, and upregulated the expression of the antiapoptotic protein, Bax. Myeloid‑derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) were markedly upregulated during tumour progression and promoted tumour growth by inhibiting the T‑cell‑mediated immune response. In vivo, a marked reduction in the MDSC ratio and tumour volume was observed in a group receiving combined treatment with LBP and IFN‑α2b in a xenograft tumour model. In conclusion, the present study suggested that the combination of LBP and IFN‑α2b is likely to be more effective in treating murine RCC compared with the less pronounced immunotherapeutic effects of administering LBP or IFN-α2b alone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides induce apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells and inhibits prostate cancer growth in a xenograft mouse model of human prostate cancer.J Med Food. 2009 Aug;12(4):695-703. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2008.1232. J Med Food. 2009. PMID: 19735167
-
Characterization of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and its effect on human hepatoma cells.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Oct;61:270-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.06.031. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 23817098
-
Synergistic effects of the immune checkpoint inhibitor CTLA-4 combined with the growth inhibitor lycorine in a mouse model of renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):21177-21186. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15505. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28416753 Free PMC article.
-
An evidence-based update on the pharmacological activities and possible molecular targets of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Dec 17;9:33-78. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S72892. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25552899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Resources industrialization channels and strategies of active polysaccharide from Lycii Fructus based on analysis of domestic and foreign intellectual properties].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Dec;41(23):4285-4291. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20162301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28933102 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Fraction From Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Reduces Immunotoxicity and Enhances Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin in Mice.Integr Cancer Ther. 2018 Sep;17(3):860-866. doi: 10.1177/1534735417753544. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Integr Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29355051 Free PMC article.
-
MYC Oncogene: A Druggable Target for Treating Cancers with Natural Products.Aging Dis. 2024 Apr 1;15(2):640-697. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0520. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37450923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides inhibit proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cell lines BIU87 by suppressing Pi3K/AKT pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):5936-5942. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13963. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27992374 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Immune-Related Seventeen-Gene Signature for Predicting Early Stage Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 11;12:665407. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665407. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177903 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Dietary Supplementation with Goji Berries (Lycium barbarum) on Microbiological Quality, Physico-Chemical, and Sensory Characteristics of Rabbit Meat.Foods. 2020 Oct 16;9(10):1480. doi: 10.3390/foods9101480. Foods. 2020. PMID: 33081259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paly JJ, Hallemeier CL, Biggs PJ, Niemierko A, Roeder F, Martínez-Mong R, Whitson J, Calvo FA, Fastner G, Sedlmayer F, et al. Outcomes in a multi-institutional cohort of patients treated with intraoperative radiation therapy for advanced or recurrent renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88:618–623. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.11.207. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Richey SL, Tamboli P, Ng CS, Lin E, Lim ZD, Araujo JC, Jonasch E, Sharma P, Pagliaro LC, Tannir NM. Phase II trial of pemetrexed plus gemcitabine in patients with locally advanced and metastatic nonclear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:450–454. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3182546a91. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

