Trajectory and Predictors of Depression and Anxiety Disorders in Mothers With the FMR1 Premutation
- PMID: 26300270
- PMCID: PMC4733592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.07.015
Trajectory and Predictors of Depression and Anxiety Disorders in Mothers With the FMR1 Premutation
Abstract
Background: Although the FMR1 premutation is associated with elevated prevalence of psychiatric disorders, the longitudinal course of symptoms has not been established. The present study followed a sample of women with the FMR1 premutation to characterize the incidence, stability, and predictors of mood and anxiety disorders across a 3-year period.
Methods: Participants included 83 women with the FMR1 premutation (mean age = 38.35) who completed the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders at two time points, 3 years apart. Additional information was obtained regarding demographic, child, and biomedical (e.g., medication, menopause, CGG repeats) factors.
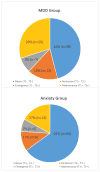
Results: We found increased prevalence of major depressive disorder (MDD) and anxiety disorders over time, with adverse outcomes predicted by complex interactions among biological, behavioral, and environmental risk factors. Lifetime MDD increased from 46% to 54% and lifetime anxiety disorders increased from 28% to 35%. Midrange CGG repeats, elevated child problem behaviors, and divorced marital status conveyed elevated risk for psychiatric diagnoses. Primary ovarian insufficiency was highly prevalent (41%) but did not account for elevated rates of psychiatric diagnoses. Medication use was highly reported (41%), particularly in women with MDD or anxiety, with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors reported as the most commonly used medication across diagnostic groups.
Conclusions: The elevated prevalence of depression and anxiety in women with the FMR1 premutation is a clear and pressing concern given the frequent occurrence of the FMR1 premutation in the general community and the adverse outcomes-at both individual and systems levels-associated with psychiatric disorders in this population.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; FMR1 premutation; Fragile X; Longitudinal.
Copyright © 2016 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Psychopathology Increases With Age in Fragile X Carrier Mothers.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 May 15;79(10):790-791. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.03.1052. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27130851 No abstract available.
References
-
- Roberts JE, Bailey DB, Mankowski J, Ford A, Sideris J, Weisenfeld LA, et al. Mood and anxiety disorders in females with the FMR1 premutation. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2009;150B:130–9. - PubMed
-
- First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, William JBW. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, (SCID-I) Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Press, Inc; 1996.
-
- Hessl D, Tassone F, Loesch DZ, Berry-Kravis E, Leehey Ma, Gane LW, et al. Abnormal elevation of FMR1 mRNA is associated with psychological symptoms in individuals with the fragile X premutation. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;139B:115–21. - PubMed
-
- Bailey DB, Sideris J, Roberts J, Hatton D. Child and genetic variables associated with maternal adaptation to fragile X syndrome: a multidimensional analysis. Am J Med Genet A. 2008;146A:720–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical