Clays as dietary supplements for swine: A review
- PMID: 26301092
- PMCID: PMC4546348
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-015-0037-9
Clays as dietary supplements for swine: A review
Abstract
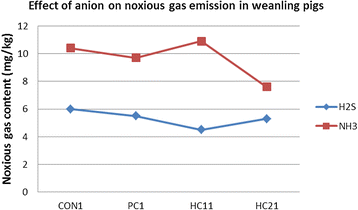
Clays are crystalline, hydrated aluminosilicate molecules composed of alkali and alkaline earth cations along with small amounts of various other elements. The best-known are montmorillonite, smectite, illite, kaolinite, biotite and clinoptilolite. The molecules in these clays are arranged in three-dimensional structures creating internal voids and channels capable of trapping a wide variety of molecules. As a result of this structure, clay minerals are regarded as a simple and effective tool for the prevention of the negative effects of many toxic compounds. Dietary supplementation with clays has been shown to improve weight gain and feed conversion in pigs. Where improvements in performance have been noted, one of the most likely explanations for the improvement is the fact clays increase nutrient digestibility. Clays reduce the speed of passage of feed along the digestive tract which allows more time for digestion. Feeding clays also causes morphological changes in the intestinal mucosa such as an increase in villus height and an increase in the villus height to crypt depth ratio. These changes increase the surface area of the gastrointestinal tract thus increasing nutrient digestibility. Several studies have indicated that feeding clay reduces the incidence, severity and duration of diarrhea in pigs. The mechanism for the reduction in diarrhea is likely due to increases in the numbers of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus and decreases in Clostridia and E. coli in the small intestine of pigs fed clays. In addition, the numbers of pigs born alive and weaned, birth weight and weaning weight have been shown to be higher for sows fed clays. Several studies have indicated that clays can help mitigate the effects of mycotoxins. The aim of the present review is to focus on the various clays which have been given attention in recent research and to discuss their potential to improve pig performance.
Keywords: Animal production; Clay; Clinoptilolite; Feed additive; Montmorillonite; Zeolite.
Figures
References
-
- Turner JL, Pas S, Dritz SS, Minton JE. Review: Alternatives to conventional antimicrobials in swine diets. Prof Anim Sci. 2001;25:217–26.
-
- Vondruskova H, Slamova R, Trckova M, Zraly Z, Pavli I. Alternatives to antibiotic growth promotors in prevention of diarrhea in weaned piglets: A review. Vet Med. 2010;55:199–224.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

