Autologous Graft Thickness Affects Scar Contraction and Quality in a Porcine Excisional Wound Model
- PMID: 26301157
- PMCID: PMC4527642
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000426
Autologous Graft Thickness Affects Scar Contraction and Quality in a Porcine Excisional Wound Model
Abstract
Background: Texture, color, and durability are important characteristics to consider for skin replacement in conspicuous and/or mobile regions of the body such as the face, neck, and hands. Although autograft thickness is a known determinant of skin quality, few studies have correlated the subjective and objective characters of skin graft healing with their associated morphologic and cellular profiles. Defining these relationships may help guide development and evaluation of future skin replacement strategies.
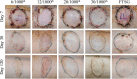
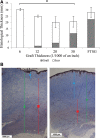
Methods: Six-centimeter-diameter full-thickness wounds were created on the back of female Yorkshire pigs and covered by autografts of variable thicknesses. Skin quality was assessed on day 120 using an observer scar assessment score and objective determinations for scar contraction, erythema, pigmentation, and surface irregularities. Histological, histochemical, and immunohistochemical assessments were performed.
Results: Thick grafts demonstrated lower observer scar assessment score (better quality) and decreased erythema, pigmentation, and surface irregularities. Histologically, thin grafts resulted in scar-like collagen proliferation while thick grafts preserves the dermal architecture. Increased vascularity and prolonged and increased cellular infiltration were observed among thin grafts. In addition, thin grafts contained predominately dense collagen fibers, whereas thick grafts had loosely arranged collagen. α-Smooth muscle actin staining for myofibroblasts was observed earlier and persisted longer among thinner grafts.
Conclusions: Graft thickness is an important determinant of skin quality. High-quality skin replacements are associated with preserved collagen architecture, decreased neovascularization, and decreased inflammatory cellular infiltration. This model, using autologous skin as a metric of quality, may give a more informative analysis of emerging skin replacement strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Nitzschke SL, et al. Wound healing trajectories in burn patients and their impact on mortality. J Burn Care Res. 2014;35:474–9. - PubMed
-
- Padgett EC. Indications for determination of the thickness of split skin grafts. Am J Surg. 1946;72:683–693. - PubMed
-
- Engrav LH, Heimbach DM, Walkinshaw MD, et al. Excision of burns of the face. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;77:744–751. - PubMed
-
- Draaijers LJ, Tempelman FR, Botman YA, et al. The patient and observer scar assessment scale: a reliable and feasible tool for scar evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113:1960–1965; discussion 1966–1967. - PubMed
-
- Rich L, Whittaker P. Collagen and Picrosirius Red staining: a polarized light assessment of fibrillar hue and spatial distribution. Braz J Morphol Sci. 2005;22:97–104.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
