Meta-analysis of shared genetic architecture across ten pediatric autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 26301688
- PMCID: PMC4863040
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3933
Meta-analysis of shared genetic architecture across ten pediatric autoimmune diseases
Abstract
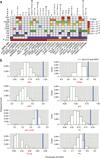
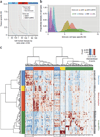
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified hundreds of susceptibility genes, including shared associations across clinically distinct autoimmune diseases. We performed an inverse χ(2) meta-analysis across ten pediatric-age-of-onset autoimmune diseases (pAIDs) in a case-control study including more than 6,035 cases and 10,718 shared population-based controls. We identified 27 genome-wide significant loci associated with one or more pAIDs, mapping to in silico-replicated autoimmune-associated genes (including IL2RA) and new candidate loci with established immunoregulatory functions such as ADGRL2, TENM3, ANKRD30A, ADCY7 and CD40LG. The pAID-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were functionally enriched for deoxyribonuclease (DNase)-hypersensitivity sites, expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs), microRNA (miRNA)-binding sites and coding variants. We also identified biologically correlated, pAID-associated candidate gene sets on the basis of immune cell expression profiling and found evidence of genetic sharing. Network and protein-interaction analyses demonstrated converging roles for the signaling pathways of type 1, 2 and 17 helper T cells (TH1, TH2 and TH17), JAK-STAT, interferon and interleukin in multiple autoimmune diseases.
Figures



Comment in
-
Genetics. Meta-analysis reveals novel overlap in genetic aetiologies of paediatric autoimmune disorders.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015 Oct;11(10):561. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.120. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26345117 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- C0482/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U24 AI086037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC1AR058606/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI061093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AR066486/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA127334/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058587/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058606/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG006830/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK085708/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG006849/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G0800759/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ETM/75/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- ETM/137/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- R18 AI048693/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HG006849/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AR047363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP3DK085708/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0800675/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA127334/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600329/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HG006830/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

