Transcriptional regulatory network during development in the olfactory epithelium
- PMID: 26303973
- PMCID: PMC4911201
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.11.177
Transcriptional regulatory network during development in the olfactory epithelium
Abstract
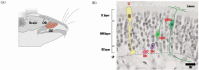
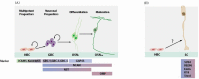
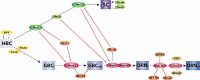
Regeneration, a process of reconstitution of the entire tissue, occurs throughout life in the olfactory epithelium (OE). Regeneration of OE consists of several stages: proliferation of progenitors, cell fate determination between neuronal and non-neuronal lineages, their differentiation and maturation. How the differentiated cell types that comprise the OE are regenerated, is one of the central questions in olfactory developmental neurobiology. The past decade has witnessed considerable progress regarding the regulation of transcription factors (TFs) involved in the remarkable regenerative potential of OE. Here, we review current state of knowledge of the transcriptional regulatory networks that are powerful modulators of the acquisition and maintenance of developmental stages during regeneration in the OE. Advance in our understanding of regeneration will not only shed light on the basic principles of adult plasticity of cell identity, but may also lead to new approaches for using stem cells and reprogramming after injury or degenerative neurological diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Canonical Notch Signaling Directs the Fate of Differentiating Neurocompetent Progenitors in the Mammalian Olfactory Epithelium.J Neurosci. 2018 May 23;38(21):5022-5037. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0484-17.2018. Epub 2018 May 8. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29739871 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and molecular regulation of neural stem cells in the olfactory epithelium.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Jun 10;306(2):309-16. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.03.027. Epub 2005 Apr 21. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15925585 Review.
-
Transcriptional and Epigenetic Control of Mammalian Olfactory Epithelium Development.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Nov;55(11):8306-8327. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0987-y. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29532253 Review.
-
Tissue plasminogen activator deficiency promotes early phase regeneration in the olfactory epithelium after bulbectomy.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013 Jun;3(6):458-67. doi: 10.1002/alr.21124. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013. PMID: 23193078
-
Embryonic Pax7-expressing progenitors contribute multiple cell types to the postnatal olfactory epithelium.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 14;30(28):9523-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0867-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20631180 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Molecular Analysis of Neural Olfactory Placode Differentiation in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2022 Sep;31(17-18):507-520. doi: 10.1089/scd.2021.0257. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Stem Cells Dev. 2022. PMID: 35592997 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2/Th2-driven inflammation impairs olfactory sensory neurogenesis in mouse chronic rhinosinusitis model.Allergy. 2019 Mar;74(3):549-559. doi: 10.1111/all.13559. Epub 2018 Dec 16. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 29987849 Free PMC article.
-
mSWI/SNF (BAF) Complexes Are Indispensable for the Neurogenesis and Development of Embryonic Olfactory Epithelium.PLoS Genet. 2016 Sep 9;12(9):e1006274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006274. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27611684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodian D, Howe HA. Experimental studies on intraneural spread of poliomyelitis virus. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital. 1941;68:248–267.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

