A research agenda for aging in China in the 21st century
- PMID: 26304837
- PMCID: PMC5179143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2015.08.003
A research agenda for aging in China in the 21st century
Abstract
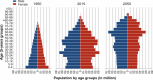
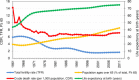
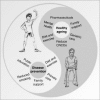
China is encountering formidable healthcare challenges brought about by the problem of aging. By 2050, there will be 400 million Chinese citizens aged 65+, 150 million of whom will be 80+. The undesirable consequences of the one-child policy, rural-to-urban migration, and expansion of the population of 'empty nest' elders are eroding the traditional family care of the elders, further exacerbating the burden borne by the current public healthcare system. The challenges of geriatric care demand prompt attention by proposing strategies for improvement in several key areas. Major diseases of the elderly that need more attention include chronic non-communicable diseases and mental health disorders. We suggest the establishment of a home care-dominated geriatric care system, and a proactive role for researchers on aging in reforming geriatric care through policy dialogs. We propose ideas for preparation of the impending aging burden and the creation of a nurturing environment conducive to healthy aging in China.
Keywords: Aging; Chronic non-communicable diseases; Geriatric care; Mental health; Pharmacological interventions; Physical exercise; Policy; Public health.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- AmericanCollegeofSportsMedicine. 2009. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
-
- Anon Diabetes in China: mapping the road ahead. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:923. - PubMed
-
- Anon A step change for tobacco control in China? Lancet. 2014;384:2000. - PubMed
-
- Bi Z., Liang X., Xu A., Wang L., Shi X., Zhao W., Ma J., Guo X., Zhang X., Zhang J. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control and sodium intake in Shandong Province, China: baseline results from Shandong-Ministry of Health Action on Salt Reduction and Hypertension (SMASH), 2011. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014;11:E88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal D., Hsiao W. Lessons from the East–China’s rapidly evolving health care system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;372:1281–1285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

