Human TYK2 deficiency: Mycobacterial and viral infections without hyper-IgE syndrome
- PMID: 26304966
- PMCID: PMC4577846
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20140280
Human TYK2 deficiency: Mycobacterial and viral infections without hyper-IgE syndrome
Abstract
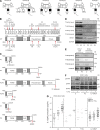
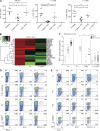
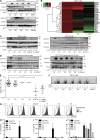
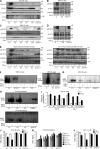
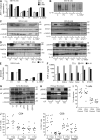
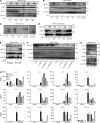
Autosomal recessive, complete TYK2 deficiency was previously described in a patient (P1) with intracellular bacterial and viral infections and features of hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES), including atopic dermatitis, high serum IgE levels, and staphylococcal abscesses. We identified seven other TYK2-deficient patients from five families and four different ethnic groups. These patients were homozygous for one of five null mutations, different from that seen in P1. They displayed mycobacterial and/or viral infections, but no HIES. All eight TYK2-deficient patients displayed impaired but not abolished cellular responses to (a) IL-12 and IFN-α/β, accounting for mycobacterial and viral infections, respectively; (b) IL-23, with normal proportions of circulating IL-17(+) T cells, accounting for their apparent lack of mucocutaneous candidiasis; and (c) IL-10, with no overt clinical consequences, including a lack of inflammatory bowel disease. Cellular responses to IL-21, IL-27, IFN-γ, IL-28/29 (IFN-λ), and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) were normal. The leukocytes and fibroblasts of all seven newly identified TYK2-deficient patients, unlike those of P1, responded normally to IL-6, possibly accounting for the lack of HIES in these patients. The expression of exogenous wild-type TYK2 or the silencing of endogenous TYK2 did not rescue IL-6 hyporesponsiveness, suggesting that this phenotype was not a consequence of the TYK2 genotype. The core clinical phenotype of TYK2 deficiency is mycobacterial and/or viral infections, caused by impaired responses to IL-12 and IFN-α/β. Moreover, impaired IL-6 responses and HIES do not appear to be intrinsic features of TYK2 deficiency in humans.
© 2015 Kreins et al.
Figures
References
-
- Beşer O.F., Conde C.D., Kutlu T., Cokuğraş F.C., Boztuğ K., and Erkan T.. 2014. Inflammatory bowel disease with lethal disease course caused by a nonsense mutation in BIRC4 encoding X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. In press. - PubMed
-
- Boisson B., Wang C., Pedergnana V., Wu L., Cypowyj S., Rybojad M., Belkadi A., Picard C., Abel L., Fieschi C., et al. . 2013. An ACT1 mutation selectively abolishes interleukin-17 responses in humans with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Immunity. 39:676–686. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.09.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boisson-Dupuis S., El Baghdadi J., Parvaneh N., Bousfiha A., Bustamante J., Feinberg J., Samarina A., Grant A.V., Janniere L., El Hafidi N., et al. . 2011. IL-12Rβ1 deficiency in two of fifty children with severe tuberculosis from Iran, Morocco, and Turkey. PLoS ONE. 6:e18524 10.1371/journal.pone.0018524 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

