The UVB-Stimulated Expression of Transglutaminase 1 Is Mediated Predominantly via the NFκB Signaling Pathway: New Evidence of Its Significant Attenuation through the Specific Interruption of the p38/MSK1/NFκBp65 Ser276 Axis
- PMID: 26305102
- PMCID: PMC4549294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136311
The UVB-Stimulated Expression of Transglutaminase 1 Is Mediated Predominantly via the NFκB Signaling Pathway: New Evidence of Its Significant Attenuation through the Specific Interruption of the p38/MSK1/NFκBp65 Ser276 Axis
Abstract
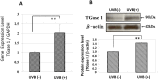
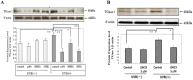
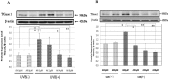
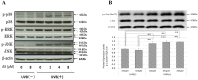
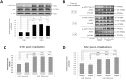
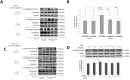
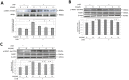
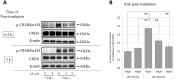
The influence of ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation on transglutaminase 1 (TGase 1), a major factor that regulates skin keratinization, has not been sufficiently characterized especially at the gene or protein level. Thus, we determined whether UVB affects the expression of TGase 1 in human keratinocytes and clarified the intracellular stress signaling mechanism(s) involved. Exposure of human keratinocytes to UVB significantly up-regulated the expression of TGase 1 at the gene and protein levels. Treatment with inhibitors of p38, MEK, JNK or NFκB significantly abolished the UVB-stimulated protein expression of TGase 1. Treatment with astaxanthin immediately after UVB irradiation did not attenuate the increased phosphorylation of Ser536/Ser468NFκBp65, c-Jun, ATK-2 and CK2, and did not abrogate the increased or diminished protein levels of c-Jun/c-Fos or I-κBα, respectively. However, the same treatment with astaxanthin significantly abolished the UVB-stimulated expression of TGase 1 protein, which was accompanied by the attenuated phosphorylation of Thr565/Ser376/Ser360MSK1, Ser276NFκBp65 and Ser133CREB. The MSK1 inhibitor H89 significantly down-regulated the increased protein expression of TGase 1 in UVB-exposed human keratinocytes, which was accompanied by an abrogating effect on the increased phosphorylation of Ser276NFκBp65 and Ser133CREB but not Thr565/Ser376/Ser360MSK1. Transfection of human keratinocytes with MSK1 siRNA suppressed the UVB-stimulated protein expression of TGase 1. These findings suggest that the UVB-stimulated expression of TGase 1 is mediated predominantly via the NFκB pathway and can be attenuated through a specific interruption of the p38/MSK1/NFκBp65Ser276 axis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Astaxanthin attenuates the UVB-induced secretion of prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-8 in human keratinocytes by interrupting MSK1 phosphorylation in a ROS depletion-independent manner.Exp Dermatol. 2012 Jul;21 Suppl 1:11-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01496.x. Exp Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22626465
-
UVB Stimulates the Expression of Endothelin B Receptor in Human Melanocytes via a Sequential Activation of the p38/MSK1/CREB/MITF Pathway Which Can Be Interrupted by a French Maritime Pine Bark Extract through a Direct Inactivation of MSK1.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 1;10(6):e0128678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128678. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26030901 Free PMC article.
-
In situ demonstration of phosphorylated c-jun and p38 MAP kinase in epidermal keratinocytes following ultraviolet B irradiation of human skin.J Pathol. 2001 Feb;193(2):248-55. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH780>3.0.CO;2-Y. J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11180173
-
Signaling Cascades Activated by UVB in Human Melanocytes Lead to the Increased Expression of Melanocyte Receptors, Endothelin B Receptor and c-KIT.Photochem Photobiol. 2018 May;94(3):421-431. doi: 10.1111/php.12848. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Photochem Photobiol. 2018. PMID: 28977677 Review.
-
Intracellular Signaling Mechanisms Involved in the Biological Effects of the Xanthophyll Carotenoid Astaxanthin to Prevent the Photo-aging of the Skin in a Reactive Oxygen Species Depletion-independent Manner: The Key Role of Mitogen and Stress-activated Protein Kinase 1.Photochem Photobiol. 2019 Mar;95(2):480-489. doi: 10.1111/php.13034. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Photochem Photobiol. 2019. PMID: 30317634 Review.
Cited by
-
The Inhibitory Effects of Anti-Oxidants on Ultraviolet-Induced Up-Regulation of the Wrinkling-Inducing Enzyme Neutral Endopeptidase in Human Fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 20;11(9):e0161580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161580. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27648570 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Inhibitor Combinations on Lysophosphatidic Acid-Mediated Chemokine Secretion in Unprimed and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Primed Synovial Fibroblasts.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Nov 21;8:848. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00848. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29209219 Free PMC article.
-
The skin protective effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Apr;42(2):218-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.03.007. Epub 2017 Mar 25. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 29719469 Free PMC article.
-
The interleukin-1α stimulated expression of the wrinkle-inducing elastase neprilysin in adult human dermal fibroblasts is mediated via the intracellular signaling axis of ERK/JNK/c-Jun/c-Fos/AP-1.J Dermatol. 2025 Jan;52(1):24-34. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.17520. Epub 2024 Oct 31. J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39482861 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase 2 mediates UV-induced skin inflammation by enhancing inflammatory cytokine production.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 26;8(10):e3148. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.550. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29072680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Del Bino S, Vioux C, Rossio-Pasquier P, Jomard A, Demarchez M, Asselineau D, et al. Ultraviolet B induces hyperproliferation and modification of epidermal differentiation in normal human skin grafted on to nude mice. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150: 658–667. - PubMed
-
- Takagi Y, Nakagawa H, Kondo H, Takema Y, Imokawa G. Levels of covalently bound ceramide are associated with UVB-induced perturbation of the skin barrier. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123: 1102–1109. - PubMed
-
- Reichert U, Michel S, Schmidt R. in Molecular Biology of the Skin The Keratinocyte, eds. Darmon M. & Bloomberg M. (Academic, San Diego: ), 1993; pp. 107–50.
-
- Kim HC, Idler WW, Kim IG, Han JH, Chung SI, Steinert PM. The complete amino acid sequence of the human transglutaminase enzyme deduced from the nucleic acid sequences of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1991;266: 536–539. - PubMed
-
- Candi E, Melino G, Mei G, Tarcsa E, Chung SI, Marekov LN, et al. Biochemical, structural, and transglutaminase substrate properties of human loricrin, the major epidermal cornified cell envelope protein. J Biol Chem. 1995;270: 26382–26390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

