Fyn Activation of mTORC1 Stimulates the IRE1α-JNK Pathway, Leading to Cell Death
- PMID: 26306048
- PMCID: PMC4598989
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.687020
Fyn Activation of mTORC1 Stimulates the IRE1α-JNK Pathway, Leading to Cell Death
Abstract
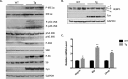
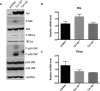
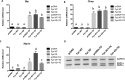
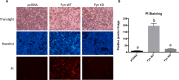
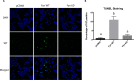
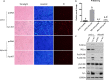
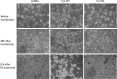
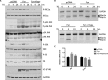
We previously reported that the skeletal muscle-specific overexpression of Fyn in mice resulted in a severe muscle wasting phenotype despite the activation of mTORC1 signaling. To investigate the bases for the loss of muscle fiber mass, we examined the relationship between Fyn activation of mTORC1, JNK, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Overexpression of Fyn in skeletal muscle in vivo and in HEK293T cells in culture resulted in the activation of IRE1α and JNK, leading to increased cell death. Fyn synergized with the general endoplasmic reticulum stress inducer thapsigargin, resulting in the activation of IRE1α and further accelerated cell death. Moreover, inhibition of mTORC1 with rapamycin suppressed IRE1α activation and JNK phosphorylation, resulting in protecting cells against Fyn- and thapsigargin-induced cell death. Moreover, rapamycin treatment in vivo reduced the skeletal muscle IRE1α activation in the Fyn-overexpressing transgenic mice. Together, these data demonstrate the presence of a Fyn-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress that occurred, at least in part, through the activation of mTORC1, as well as subsequent activation of the IRE1α-JNK pathway driving cell death.
Keywords: Fyn; IRE1α; c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK); cell death; endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress); mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); skeletal muscle.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glucose amplifies fatty acid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic beta-cells via activation of mTORC1.PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004954. Epub 2009 Mar 23. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19305497 Free PMC article.
-
RNF13, a RING finger protein, mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through the inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE1α)/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8726-8736. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.368829. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23378536 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α links palmitate-induced mTOR activation and lipotoxicity in hepatocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):C1130-C1140. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00165.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33052067 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity may be therapeutically targeted by natural and chemical compounds: A review.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Feb;164:105383. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105383. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33348022 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes.Cells. 2020 Mar 13;9(3):706. doi: 10.3390/cells9030706. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32183037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CO-Releasing Molecule-2 Prevents Acute Kidney Injury through Suppression of ROS-Fyn-ER Stress Signaling in Mouse Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jul 6;2021:9947772. doi: 10.1155/2021/9947772. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34326922 Free PMC article.
-
The fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase TIGAR suppresses NF-κB signaling by directly inhibiting the linear ubiquitin assembly complex LUBAC.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 18;293(20):7578-7591. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002727. Epub 2018 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29650758 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn Kinase: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Kidney Injury.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020 May 1;28(3):213-221. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.214. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32336052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 8;19(3):778. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030778. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29518028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hetz C. (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 89–102 - PubMed
-
- Bernales S., Papa F. R., Walter P. (2006) Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22, 487–508 - PubMed
-
- Ron D., Walter P. (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 519–529 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

