Revision Upper Blepharoplasty
- PMID: 26306087
- PMCID: PMC4536059
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1556844
Revision Upper Blepharoplasty
Abstract
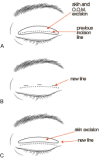
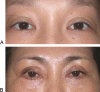
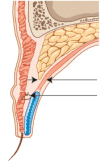
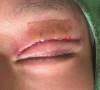
The ideal shape and height of the double eyelid varies widely depending on the patient and the culture. Patients may be dissatisfied after a double eyelid operation for the following reasons: scar, low versus high fold, shallow versus deep fold, triple folds, pretarsal fullness, ptosis, and asymmetry. Here the author describes the complications experienced after double eyelid surgery and corrective procedures.
Keywords: complication of double eyelid operation; revision blepharoplasty.
Figures






References
-
- Cho I C The Art of Blepharoplasty Seoul, South Korea: Koonja Publishing; 201384–124. (in Korean)
-
- Chang S H, Chen W P, Cho I C, Ahn T J. Comprehensive review of Asian cosmetic upper eyelid oculoplastic surgery: Asian blepharoplasty and the like. Arch Aesthet Plast Surg. 2014;20(3):129–139.
-
- Chen W P. The concept of a glide zone as it relates to upper lid crease, lid fold, and application in upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119(1):379–386. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y W, Park H J, Kim S. Revision of unfavorable double eyelid operation by repositioning of preaponeurotic fat. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;27:99–104.
-
- Lew D H, Kang J H, Cho I C. Surgical correction of multiple upper eyelid folds in East Asians. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127(3):1323–1331. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

