Effects of hexanic extract of Serenoa repens (Permixon® 160 mg) on inflammation biomarkers in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 26306400
- PMCID: PMC5049653
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.23059
Effects of hexanic extract of Serenoa repens (Permixon® 160 mg) on inflammation biomarkers in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
Background: Chronic prostatic inflammation (CPI) could be a cause of symptomatic or complicated benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). In previous in vitro and in vivo studies, Hexanic Extract of Serenoa repens (HESr) namely Permixon(®) has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory properties. With the aim to provide new insight onto HESr anti-inflammatory properties in human we explore its effect on CPI biomarkers in men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) related to BPH using a non-invasive method and investigate links between biomarkers and clinical symptoms.
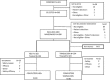
Methods: An international, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, tamsulosin-controlled study was carried out in 206 men with BPH-related LUTS. Patients received oral daily HESr 320mg or tamsulosin 0.4 mg during 3 months. The first urine stream after digital rectal examination (DRE) was collected at Day 1 and Day 90 and mRNA was extracted from prostatic epithelial cells desquaming in the lumen of the glands and seminal plasma fluid after DRE. mRNA quantification of the 29 most significant published inflammation markers in BPH and protein detection in urine was performed.
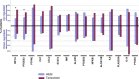
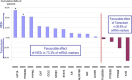
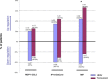
Results: At D90, a decrease in mean gene expression was observed for 65.4% of the markers detected in the HESr group versus 46.2% in the tamsulosin group. In the 15 most frequently expressed genes, this difference was higher (80% vs. 33% respectively). Three proteins (MCP-1/CCL2, IP-10/CXCL10, and MIF) were detected. At D90, a decrease in the number of patients who expressed MCP-1/CCL2 and IP-10/CXCL10 was observed only in the HESr group. Moreover, MIF expression was significantly reduced by HESr compared with tamsulosin (P = 0.007). Finally, in contrast to tamsulosin, the subgroup of patients treated by HESr and who over expressed MIF at baseline, had a higher response to the International Prostate Symptom Score (I-PSS) than those who did not over express this protein (mean I-PSS change: -6.4 vs. -4.5 respectively). As the study is exploratory, results should be confirmed in a powered clinical study.
Conclusions: These results showed for the first time at clinical level the anti-inflammatory properties of HESr, already indicated in BPH-related LUTS. Thus, HESr could be of interest to prevent unfavourable evolution in patients with CPI.
Keywords: benign prostatic hyperplasia; chronic prostatic inflammation; hexanic extract of serenoa repens; lower urinary tract symptoms; permixon®.
© 2015 The Authors. The Prostate Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Ficarra V, Rossanese M, Zazzara M, Giannarini G, Abbinante M, Bartoletti R, Mirone V, Scaglione F. The role of inflammation in lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) due to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and its potential impact on medical therapy. Curr Urol Rep 2014; 15:463–469. - PubMed
-
- Gandaglia G, Briganti A, Gontero P, Mondeni N, Novara G, Salonia A, Sciarra A, Montorsi F. The role of chronic prostatic inflammation in the pathogenesis and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int 2013; 112:432–441. - PubMed
-
- Zlotta AR, Egawa S, Pushkar D, Govorov A, Kimura T, Kido M, Takahashi H, Kuk C, Kovylina M, Aldaoud N, Fleshner N, Finelli A, Klotz L, Lockwood G, Sykes J, Kwast Tv.. Prevalence of inflammation and benign prostatic hyperplasia on autopsy in Asian and Caucasian men. Eur Urol 2014; 66:619–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

