Endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer: current status, possible mechanisms and overcoming strategies
- PMID: 26306654
- PMCID: PMC5558537
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc.15.93
Endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer: current status, possible mechanisms and overcoming strategies
Abstract
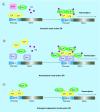
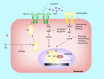
Endocrine therapy has become one of most effective forms of targeted adjuvant therapy for hormone-sensitive breast cancer and may be given after surgery or radiotherapy, and also prior, or subsequent to chemotherapy. Current commonly used drugs for adjuvant endocrine therapy can be divided into following three classes: selective estrogen receptor modulators, aromatase inhibitors and selective estrogen receptor downregulators. Tumor cells can develop resistance to endocrine therapy, a major obstacle limiting the success of breast cancer treatment. The complicated crosstalk, both genomic and nongenomic, between estrogen receptors and growth factors was considered to be a crucial factor contributing to endocrine resistance. However, resistance to this therapy is thought to be a progressive, step-wise process, and the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this review, we summarize the possible biological and molecular mechanisms that underlie endocrine resistance, and discuss some novel strategies to overcoming these issues.
Keywords: breast cancer; drug resistance; endrocrine therapeutics; estrogen receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported in part by NNSF Grants (81071880 and 30973456 to W Fan), and NIH CA92880 (to W Fan). The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Chang J, Sui M, Fan W. Estrogen receptor alpha attenuates therapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel on breast xenograft tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012;134(3):969–980. - PubMed
-
- Sui M, Huang Y, Park BH, Davidson NE, Fan W. Estrogen receptor alpha mediates breast cancer cell resistance to paclitaxel through inhibition of apoptotic cell death. Cancer Res. 2007;67(11):5337–5344. - PubMed
-
- Sui M, Jiang D, Hinsch C, Fan W. Fulvestrant (ici 182,780) sensitizes breast cancer cells expressing estrogen receptor alpha to vinblastine and vinorelbine. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010;121(2):335–345. - PubMed
-
- Schwartzberg LS, Wang G, Somer BG, et al. Phase ii trial of fulvestrant with metronomic capecitabine for postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, her2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer. 2014;14(1):13–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
