The prevalence of benign prostatic hyperplasia in mainland China: evidence from epidemiological surveys
- PMID: 26306721
- PMCID: PMC4549711
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13546
The prevalence of benign prostatic hyperplasia in mainland China: evidence from epidemiological surveys
Abstract
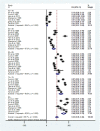
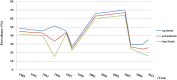
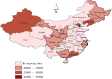
The epidemiological characteristics of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) in mainland China are not completely understood. We performed this meta-analysis to assess the prevalence of BPH from 1989 through 2014. A total of 14 articles and 19 datasets were included. The pooled overall prevalence of BPH among men aged 40 years and older was 36.6% [95% CI, 32.3-44.8]. The occurrence rate of BPH in the age groups 40-49 years, 50-59 years, 60-69 years, 70-79 years and 80 years and older was 2.9%, 29.0%, 44.7%, 58.1% and 69.2%, respectively. The pooled occurrence rate of BPH was 41.5% [95% CI, 34.5-48.4] in urban areas and 38.6% [95% CI, 22.7-54.6] in rural areas; this difference in prevalence was not statistically significant [OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 0.97-2.36]. BPH is highly prevalent in mainland China, and its prevalence increased with age. The trend in the prevalence of BPH in mainland China was not steady; the prevalence map based on a geographic information system (GIS) showed an unequal geographic distribution. High-quality surveys on BPH with a larger sample size are needed throughout mainland China to confirm these findings.
Figures



References
-
- Wei J. T., Calhoun E. & Jacobsen S. J. Urologic diseases in America project: benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 173, 1256–61 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Calais Da Silva F. et al. Relative importance of sexuality and quality of life in patients with prostatic symptoms. Results of an international study. Eur Urol 31, 272–80 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

