Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection versus conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26307050
- PMCID: PMC4549869
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-015-0096-y
Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection versus conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a randomized controlled trial
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection versus conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a randomized controlled trial.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2017 Aug 11;15(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12958-017-0279-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28800745 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) is still proposed and employed in the clinical practice to improve the reproductive outcome in infertile couples scheduled for conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection (cICSI). The aim of the current randomized controlled trial (RCT) was to test the hypothesis that IMSI gives a better live birth delivery rate than cICSI.
Methods: Infertile couples scheduled for their first cICSI cycle for male factor were allocated using a simple randomization procedure. All available biological and clinical data were recorded and analyzed in a triple-blind fashion.
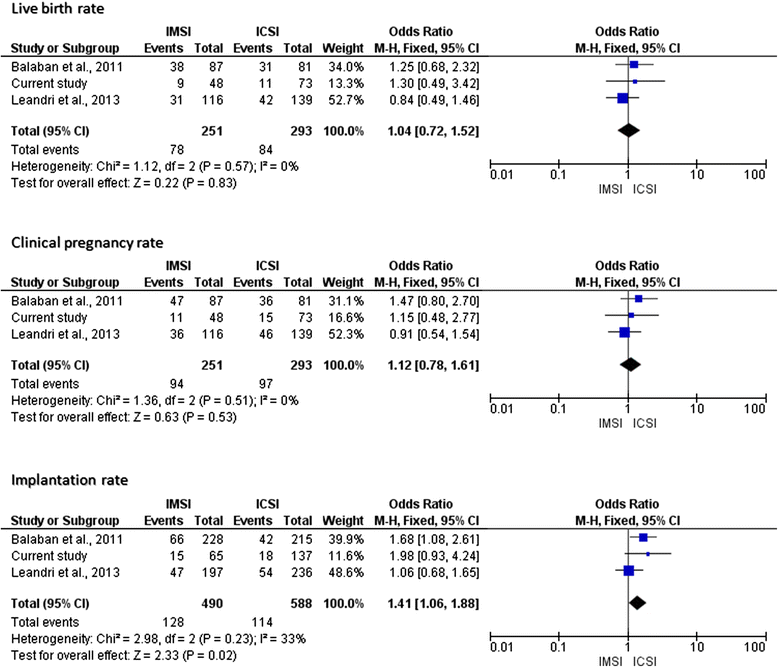
Results: Our final analysis involved the first 121 patients (48 and 73 subjects for IMSI and cICSI arm, respectively) because the trial was stopped prematurely on the advice of the data safety and monitoring Committee because of concerns about IMSI efficacy at the first interim analysis. No significant difference between arms was detected in rates of clinical pregnancy per embryo transferred [11/34 (32.3%) vs. 15/64 (23.4%); odds ratio (OR) 1.56, 95% (confidence interval) CI 0.62-3.93, P = 0.343] and of live birth delivery [9/48 (18.8%) vs. 11/73 (15.1%); OR 1.30, 95%CI 0.49-3.42, P = 0.594).
Conclusion: Current data did not support the routine use of IMSI in the clinical practice for improving cICSI results in unselected infertile couples with male factor.
Figures
References
-
- Bartoov B, Berkovitz A, Eltes F, Kogosowski A, Menezo Y, Barak Y. Real-time fine morphology of motile human sperm cells is associated with IVF-ICSI outcome. J Androl. 2002;23:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources