Selective repression of RET proto-oncogene in medullary thyroid carcinoma by a natural alkaloid berberine
- PMID: 26307103
- PMCID: PMC4549123
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1610-5
Selective repression of RET proto-oncogene in medullary thyroid carcinoma by a natural alkaloid berberine
Abstract
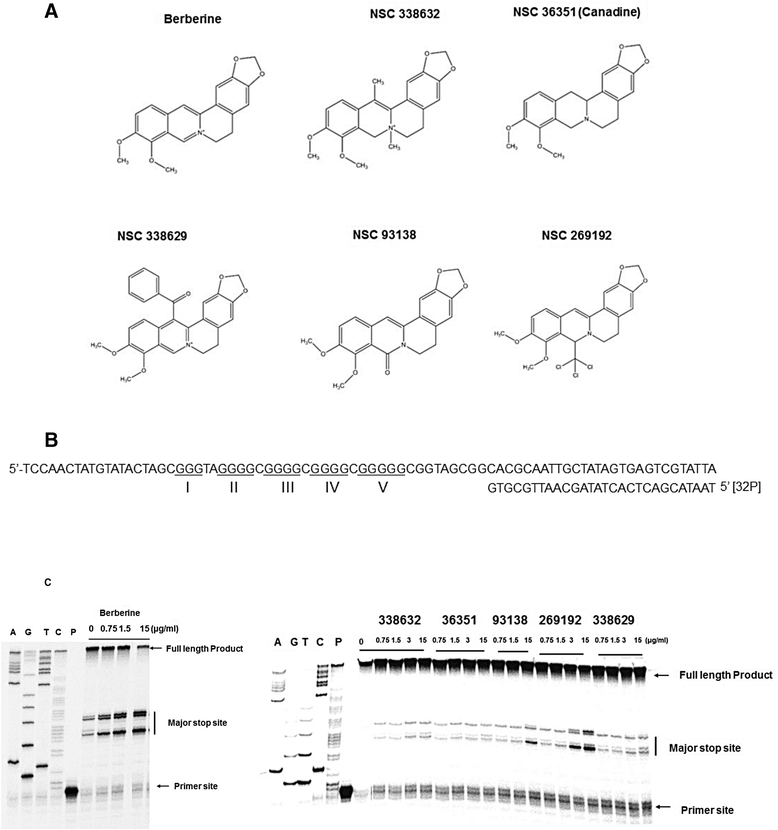
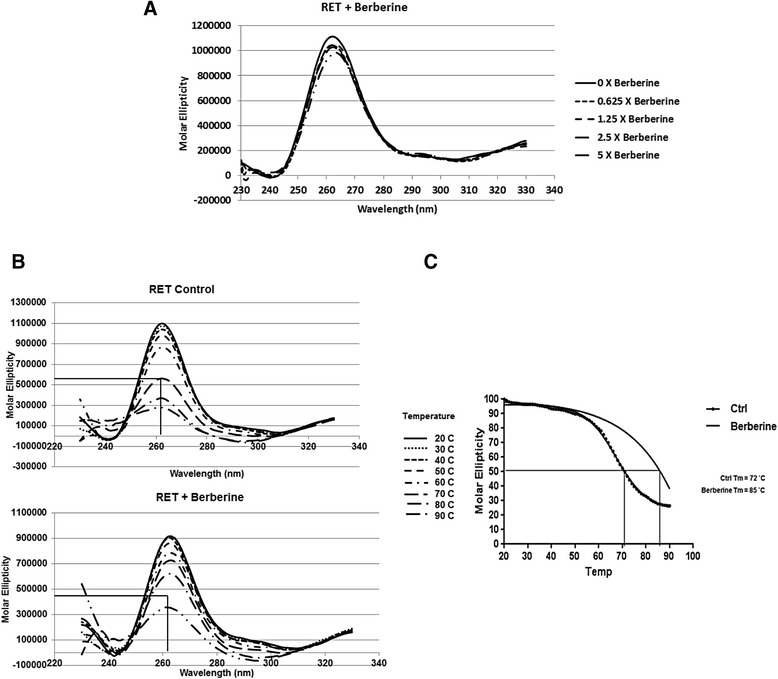
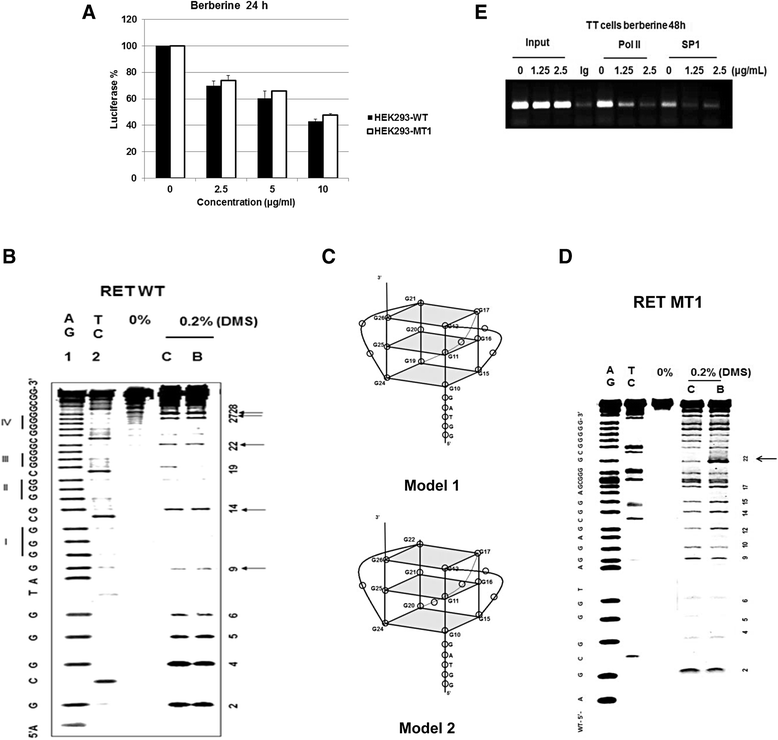
Background: The gain-of-function mutation of the RET proto-oncogene, which encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase, is strongly associated with the development of several medullary thyroid carcinomas (MTCs). Thus, the RET protein has been explored as an excellent target for progressive and advanced MTC. In this study we have demonstrated a therapeutic strategy for MTC by suppressing the transcription of RET proto-oncogene though the stabilization of G-quadruplex structure formed on the promoter region of this gene using a natural product berberine.
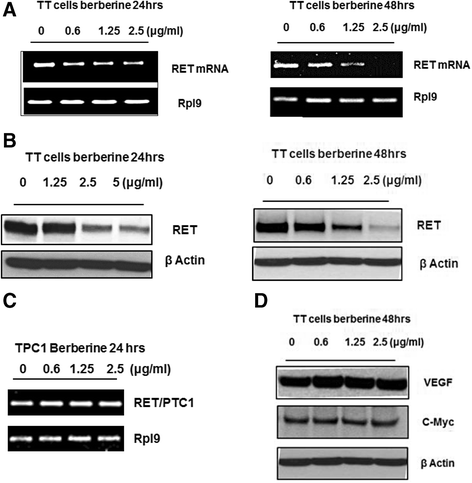
Methods: Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) TT cell line has been used to evaluate the effects of berberine on RET expression and its downstream signaling pathways. The specificity of berberine was demonstrated by using the papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC1 cell line, which lacks the G-quadruplex forming sequence on the RET promoter region due to chromosomal rearrangement.
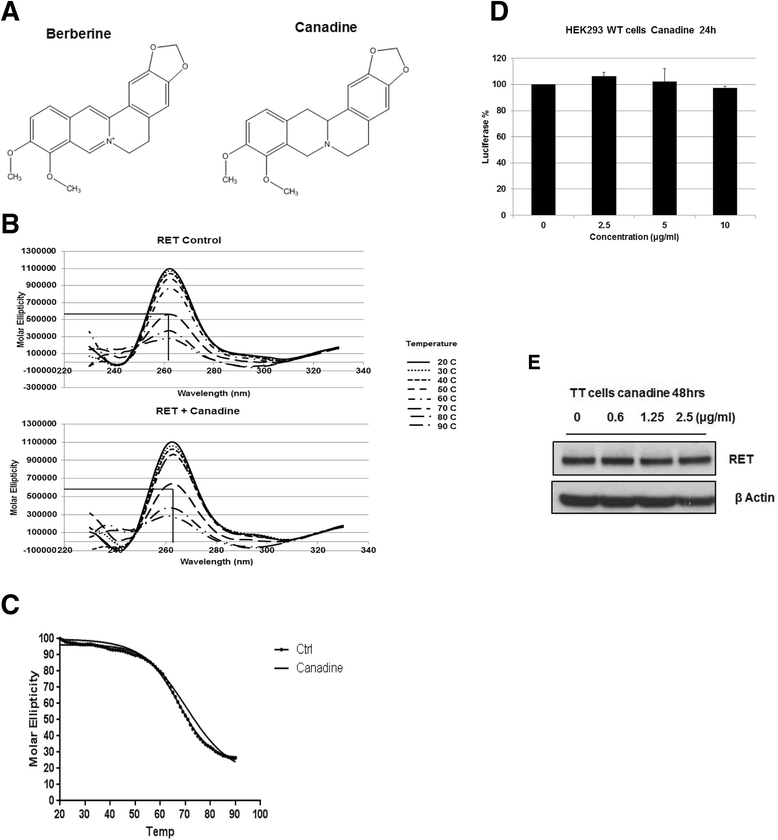
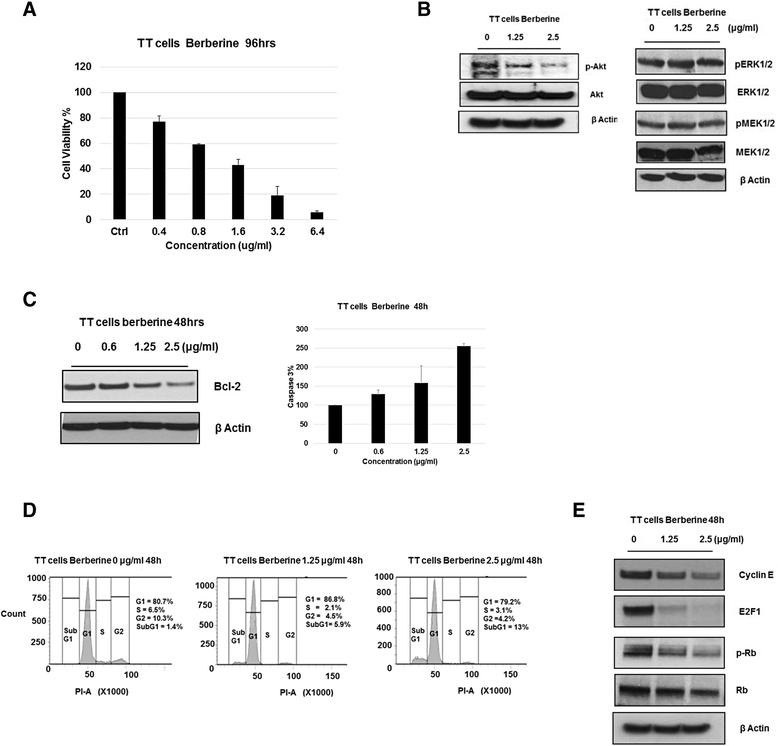
Results: Berberine suppressed the RET expression by more than 90 % in MTC TT cells at a concentration of 2.5 μg/ml with minimal effect on the TPC1 cells. Canadine, which is a structural analogue of berberine, showed little interaction with RET G-quadruplex and also had no effect on RET expression in MTC TT cells. The down-regulation of RET with berberine further inhibited the cell proliferation through cell cycle arrest and activation of apoptosis in TT cells, which was confirmed by a 2-fold increase in the caspase-3 activity and the down-regulation of cell-cycle regulatory proteins.
Conclusion: Our data strongly suggest that the G-quadruplex forming region and the stabilization of this structure play a critical role in mediating the repressive effect of berberine on RET transcription.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Z, Qi X, Fei J, Yu X, Zhao Y, Zhao J, Jin H, Wang J, Ying R, Zhang X. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A caused by a p.C618R RET proto-oncogene mutation in a Chinese pedigree. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2014;31(3):348–351. - PubMed
-
- Carter MT, Yome JL, Marcil MN, Martin CA, Vanhorne JB, Mulligan LM. Conservation of RET proto-oncogene splicing variants and implications for RET isoform function. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 2001;95(3–4):169–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

