Sandcastle: software for revealing latent information in multiple experimental ChIP-chip datasets via a novel normalisation procedure
- PMID: 26307543
- PMCID: PMC4549617
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13395
Sandcastle: software for revealing latent information in multiple experimental ChIP-chip datasets via a novel normalisation procedure
Abstract
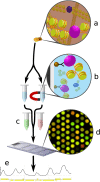
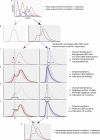
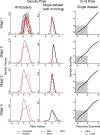
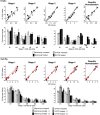
ChIP-chip is a microarray based technology for determining the genomic locations of chromatin bound factors of interest, such as proteins. Standard ChIP-chip analyses employ peak detection methodologies to generate lists of genomic binding sites. No previously published method exists to enable comparative analyses of enrichment levels derived from datasets examining different experimental conditions. This restricts the use of the technology to binary comparisons of presence or absence of features between datasets. Here we present the R package Sandcastle — Software for the Analysis and Normalisation of Data from ChIP-chip AssayS of Two or more Linked Experiments — which allows for comparative analyses of data from multiple experiments by normalising all datasets to a common background. Relative changes in binding levels between experimental datasets can thus be determined, enabling the extraction of latent information from ChIP-chip experiments. Novel enrichment detection and peak calling algorithms are also presented, with a range of graphical tools, which facilitate these analyses. The software and documentation are available for download from http://reedlab.cardiff.ac.uk/sandcastle.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A novel statistical method for quantitative comparison of multiple ChIP-seq datasets.Bioinformatics. 2015 Jun 15;31(12):1889-96. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv094. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25682068 Free PMC article.
-
Software for rapid time dependent ChIP-sequencing analysis (TDCA).BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Nov 25;18(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1936-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29178831 Free PMC article.
-
Ringo--an R/Bioconductor package for analyzing ChIP-chip readouts.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun 26;8:221. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-221. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17594472 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations on Experimental Design and Data Analysis of Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Experiments.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1689:9-28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7380-4_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29027161 Review.
-
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis to Define Transcriptional Regulatory Networks.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2017;160:1-14. doi: 10.1007/10_2016_43. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28070596 Review.
Cited by
-
Global genome nucleotide excision repair is organized into domains that promote efficient DNA repair in chromatin.Genome Res. 2016 Oct;26(10):1376-1387. doi: 10.1101/gr.209106.116. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Genome Res. 2016. PMID: 27470111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren B. et al. Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science 290, 2306 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Pokholok D. et al. Genome-wide map of nucleosome acetylation and methylation in yeast. Cell 122, 517–527 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Lee W. et al. A high-resolution atlas of nucleosome occupancy in yeast. Nat Genet 39, 1235–1244 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

