Digit ratio and autism spectrum disorders in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children: a birth cohort study
- PMID: 26307613
- PMCID: PMC4550720
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007433
Digit ratio and autism spectrum disorders in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children: a birth cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate whether second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D:4D), a measure commonly used as a proxy for fetal testosterone exposure, is associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), as predicted by the extreme male brain theory of autism.
Design: A birth cohort study.
Setting: The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC).
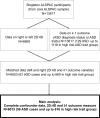
Participants: 6015 ALSPAC children with data on digit ratio, at least 1 outcome measure and information on potential confounding variables (parental occupational class, maternal education and age at digit ratio measurement). Digit ratio was measured by the photocopy and calliper method.
Outcomes: ASD diagnosis (cases were identified previously by record linkage or maternal report) and 4 measures that combine optimally within ALSPAC to predict ASD: the Children's Communication Checklist (coherence subscale), the Social and Communication Disorders Checklist, a repetitive behaviour measure, and the Emotionality, Activity and Sociability scale (sociability subscale). These measures were dichotomised, with approximately 10% defined as the 'risk' group.
Results: Using logistic regression, we examined the association of 2D:4D with ASDs and 4 dichotomised ASD traits. Covariates were occupational class, maternal education and age at 2D:4D measurement. 2D:4D was not associated with ASDs in males (adjusted OR per 1 SD increase in mean 2D:4D, 0.88 (95% CI 0.65 to 1.21), p=0.435) or females (adjusted OR=1.36 (95% CI 0.81 to 2.28), p=0.245). Similar results were observed after adjustment for IQ. There was 1 weak association between reduced coherence and increased left 2D:4D in males, in the opposite direction to that predicted by the extreme male brain theory (adjusted OR=1.15 (95% CI 1.02 to 1.29), p=0.023). Given multiple comparisons, this is consistent with chance.
Conclusions: In this population-based study, there was no strong evidence of an association between 2D:4D and ASD diagnosis or traits, although the CIs were wide. These results are not consistent with the extreme male brain theory.
Keywords: Child & adolescent psychiatry < PSYCHIATRY; Developmental neurology & neurodisability < PAEDIATRICS; EPIDEMIOLOGY.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) . Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
-
- Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network Surveillance Year 2010 Principal Investigators; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2010. MMWR Surveill Summ 2014;63:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
