PD-1 and PD-L1 Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma with Sarcomatoid Differentiation
- PMID: 26307625
- PMCID: PMC4674298
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0150
PD-1 and PD-L1 Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma with Sarcomatoid Differentiation
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies that target the programmed death-1 (PD-1)-programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) axis have antitumor activity against multiple cancers. The presence of sarcomatoid differentiation in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is associated with resistance to targeted therapy and poor responses to IL2 immunotherapy. Given the aggressive nature of RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation and the exclusion of sarcomatoid histology from metastatic RCC clinical trials, less is understood regarding selection of therapies. Here, we characterized the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation. We directly compared two PD-L1 antibodies and found concordance of PD-L1 positivity in 89% of tested RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation. Coexpression of PD-L1 on neoplastic cells and the presence of PD-1-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were identified in 50% (13 of 26) of RCCs with sarcomatoid differentiation. In contrast, only 1 of 29 clear cell RCCs (3%) had concurrent expression of PD-L1 and PD-1 (P = 0.002). Our study suggests that RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation may express PD-1/PD-L1 at a higher percentage than RCC without sarcomatoid differentiation, and patients with these tumors may be good candidates for treatment with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
D. Bryant, Z. Gatalica, and S. Reddy are employees of Caris Life Sciences. S. Z. Millis is a former employee of Caris Life Sciences. N. J. Vogelzang is consultant to Roche/Genentech and to Caris Life Sciences. T. H. Ho, R. W. Joseph, E. M. Carballido, A. H. Bryce, M. L. Stanton, and E. P. Castle have no disclosures.
Figures


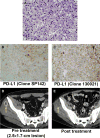
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Negrier S, et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013 May;14(6):552–62. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Erratum in: Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jun;14(7):e254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

