Aqueous Extract of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and Ferulic Acid Reduce the Expression of TNF-α and IL-1β in LPS-Activated Macrophages
- PMID: 26307961
- PMCID: PMC6332211
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200815319
Aqueous Extract of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and Ferulic Acid Reduce the Expression of TNF-α and IL-1β in LPS-Activated Macrophages
Abstract
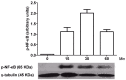
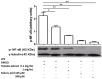
Acute inflammation is essential for defending the body against pathogens; however, when inflammation becomes chronic, it is harmful to the body and is part of the pathophysiology of various diseases such as Diabetes Mellitus type 2 (DM2) and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) among others. In chronic inflammation macrophages play an important role, mainly through the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and Interleukin (IL)-1β, explained in part by activation of the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a signaling pathway which culminates in the activation of Nuclear factor (NF)-κB, an important transcription factor in the expression of these proinflammatory genes. On the other hand, the benefits on health of a diet rich in fruit and vegetables are well described. In this work, the effects of aqueous extract of tomato and ferulic acid on the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in LPS activated monocyte-derived THP-1 macrophages were investigated. In addition, using Western blot, we investigated whether the inhibition was due to the interference on activation of NF-κB. We found that both the tomato extract and ferulic acid presented inhibitory activity on the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β cytokine by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB. The current results suggest that tomatoes and ferulic acid may contribute to prevention of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB; inflammation; macrophages; proinflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ferulic acid alleviates sciatica by inhibiting neuroinflammation and promoting nerve repair via the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Apr;29(4):1000-1011. doi: 10.1111/cns.14060. Epub 2023 Jan 4. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 36601662 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke synergizes lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α secretion from macrophages via substance P-mediated nuclear factor-κB activation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Mar;44(3):302-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0288OC. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20160043 Free PMC article.
-
DXXK exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB/COX-2 signalling pathway and the expression of inflammatory mediators.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 3;178:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26571085
-
Nauclea officinalis inhibits inflammation in LPS-mediated RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 May 13;183:159-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Jan 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26806575
-
Aloe vera downregulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production and expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):471-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23911403
Cited by
-
Standardised tomato extract as an alternative to acetylsalicylic acid in patients with primary hypertension and high cardiovascular risk - a randomised, controlled trial.Arch Med Sci. 2018 Jun;14(4):773-780. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2017.69864. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Arch Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30002694 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition of Tomato Seed Flours, and Their Radical Scavenging, Anti-Inflammatory and Gut Microbiota Modulating Properties.Molecules. 2021 Mar 9;26(5):1478. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051478. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33803186 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin mediates tomato and broccoli extract effects on glucose homeostasis in high fat diet-induced obesity in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jul 18;16:225. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1203-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27430475 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Xuebijing injection and its influence on immunomodulation in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Feb 18;20(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3204-z. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30777117 Free PMC article.
-
Fruitflow®: the first European Food Safety Authority-approved natural cardio-protective functional ingredient.Eur J Nutr. 2017 Mar;56(2):461-482. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1265-2. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Eur J Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27388464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kobayashi S.D., Voyich J.M., Burlak C., DeLeo F.R. Neutrophils in the innate immune response. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2005;53:505–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

