Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Cooperates in Zearalenone-Induced Cell Death of RAW 264.7 Macrophages
- PMID: 26307968
- PMCID: PMC4581325
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160819780
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Cooperates in Zearalenone-Induced Cell Death of RAW 264.7 Macrophages
Abstract
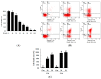
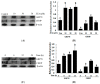
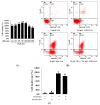
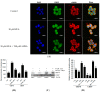
Zearalenone (ZEA) is a fungal mycotoxin that causes cell apoptosis and necrosis. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of ZEA toxicity. The objective of this study was to explore the effects of ZEA on the proliferation and apoptosis of RAW 264.7 macrophages and to uncover the signaling pathway underlying the cytotoxicity of ZEA in RAW 264.7 macrophages. This study demonstrates that the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway cooperated in ZEA-induced cell death of the RAW 264.7 macrophages. Our results show that ZEA treatment reduced the viability of RAW 264.7 macrophages in a dose- and time-dependent manner as shown by the 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay (MTT) and flow cytometry assay. Western blots analysis revealed that ZEA increased the expression of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein (CHOP), two ER stress-related marker genes. Furthermore, treating the cells with the ER stress inhibitors 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA) or knocking down CHOP, using lentivirus encoded short hairpin interfering RNAs (shRNAs), significantly diminished the ZEA-induced increases in GRP78 and CHOP, and cell death. In summary, our results suggest that ZEA induces the apoptosis and necrosis of RAW 264.7 macrophages in a dose- and time-dependent manner via the ER stress pathway in which the activation of CHOP plays a critical role.
Keywords: CHOP; RAW 264.7 macrophages; endoplasmic reticulum stress; zearalenone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mycotoxin zearalenone induces apoptosis in mouse Leydig cells via an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent signalling pathway.Reprod Toxicol. 2015 Apr;52:71-7. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Reprod Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25720297
-
Zearalenone induces apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Nov;102(11):10543-10553. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-16216. Epub 2019 Sep 5. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 31495631
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Cooperates in Silica Nanoparticles-Induced Macrophage Apoptosis via Activation of CHOP-Mediated Apoptotic Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 21;20(23):5846. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235846. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31766455 Free PMC article.
-
Zearalenone Promotes Cell Proliferation or Causes Cell Death?Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 2;10(5):184. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050184. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29724047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of stress response-related signaling and its contribution to the toxicity of zearalenone in mammals.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022 Jul;21(4):3326-3345. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12974. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022. PMID: 35751400 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of Safety of Zearalenone: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;14(6):386. doi: 10.3390/toxins14060386. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35737047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proanthocyanidin protects against acute zearalenone-induced testicular oxidative damage in male mice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Jan;24(1):938-946. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7886-4. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 27761864
-
Zearalenone Induces Endothelial Cell Apoptosis through Activation of a Cytosolic Ca2+/ERK1/2/p53/Caspase 3 Signaling Pathway.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Mar 4;13(3):187. doi: 10.3390/toxins13030187. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806711 Free PMC article.
-
Immunostimulatory Activities of Theobromine on Macrophages via the Activation of MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Sep 12;44(9):4216-4228. doi: 10.3390/cimb44090289. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36135201 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-Mediated Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Induced by Zearalenone in Mouse Sertoli Cells via ER Stress and the ATP/AMPK Pathway.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jan 1;10(1):24. doi: 10.3390/toxins10010024. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29301253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuiper G.G., Lemmen J.G., Carlsson B., Corton J.C., Safe S.H., van der Saag P.T., van der Burg B., Gustafsson J.A. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor β. Endocrinology. 1998;139:4252–4263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

