Effect of Regulatory T Cells on Promoting Apoptosis of T Lymphocyte and Its Regulatory Mechanism in Sepsis
- PMID: 26309018
- PMCID: PMC4683547
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2014.0235
Effect of Regulatory T Cells on Promoting Apoptosis of T Lymphocyte and Its Regulatory Mechanism in Sepsis
Abstract
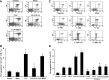
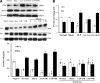
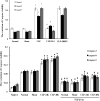
With both in vivo and in vitro experiments, the present study was conducted to investigate the effect of regulatory T cell (Treg) on promoting T-lymphocyte apoptosis and its regulatory mechanism through transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β1) signaling in mice. A murine model of polymicrobial sepsis was reproduced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP); PC61 and anti-TGF-β antibodies were used to decrease counts of CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs and inhibit TGF-β activity, respectively. Splenic CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs and CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells were isolated. Phenotypes, including cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4), forkhead/winged helix transcription factor p3 (Foxp3), and TGFβ1(m+), as well as the apoptotic rate of CD4(+)CD25(-) T cell, were analyzed by flow cytometry. Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was performed to determine mRNA expression of TGF-β1, and the expressions of Smad2/Smad3, Bcl-2 superfamily members of Bcl-2/Bim, cytochrome C, the mitochondrial membrane potential, and caspases in CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells were simultaneously determined. After treatment with PC61 or anti-TGF-β antibody, CTLA-4, Foxp3, and TGFβ1(m+) expressions of CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs were markedly decreased in comparison to that of the CLP group and the apoptosis rate of CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells was significantly positively correlated with the expression of TGF-β1. Meanwhile, levels of P-Smad2/P-Smad3, proapoptotic protein Bim, cytochrome C, and activity of caspase-3, -8, -9 were downregulated, whereas the mitochondrial membrane potential and antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 expression were restored. Taken together, our data indicated that the TGF-β1 signal could be partly involved in the apoptosis of CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells promoted by CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs, therefore inhibition of TGF-β1 expression may provide a novel strategy for the improvement of host immunosuppression following sepsis.
Figures






References
-
- Bourguet CB, Boulay PL, Claing A, Lubell WD. 2014. Design and synthesis of novel azapeptide activators of apoptosis mediated by caspase-9 in cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24(15):3361–3365 - PubMed
-
- Caraci F, Battaglia G, Busceti C, Biagioni F, Mastroiacovo F, Bosco P, Drago F, Nicoletti F, Sortino MA, Copani A. 2008. TGF-beta 1 protects against Abeta-neurotoxicity via the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway. Neurobiol Dis 30(2):234–242 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

