Association between TCF7L2 polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 26309596
- PMCID: PMC4537972
Association between TCF7L2 polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: Our aim was to investigate the relationship between transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility.
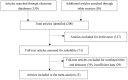
Methods: PubMed, Embase and CNKI databases were used to search the related studies investigating the correlation between TCF7L2 polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility. Pooled ORs and 95% CIs, based on five genetic models, were applied to estimate the association betweenTCF7L2 polymorphisms and breast cancer. A fixed-effect model or a random-effect model was applied according to the between-study heterogeneity.
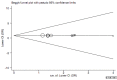
Results: We analyzed six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TCF7L2 gene, namely rs12255372, rs7903146, rs7900150, rs3750805, rs1225404 and rs7003146. The increased risk of breast cancer was associated with TCF7L2 polymorphisms (22 vs. 11: OR=1.16, 95% CI=1.02-1.32; 22+12 vs. 11: OR=1.06, 95% CI=1.02-1.10; 22 vs. 11+12: OR=1.15, 95% CI=1.04-1.27; 2 vs. 1: OR=1.07, 95% CI=1.02-1.13; 12 vs. 11: OR=1.05, 95% CI=1.01-1.09). Among the locus, rs7903146 polymorphism was significantly associated with the risk for breast cancer under five genetic models (TT vs. CC: OR=1.29, 95% CI=1.08-1.53; TT+CT vs. CC: OR=1.09, 95% CI=1.01-1.18; TT vs. CC+CT: OR=1.24, 95% CI=1.05-1.48; T vs. C: OR=1.11, 95% CI=1.04-1.19; CT vs. CC: OR=1.08, 95% CI=1.00-1.17). Additionally, rs7900150 also showed effects on the susceptibility of breast cancer (TT vs. AA: OR=1.22, 95% CI=1.07-1.39; TT+AT vs. AA: OR=1.06, 95% CI=1.00-1.14; TT vs. AA+AT: OR=1.21, 95% CI=1.07-1.37; T vs. A: OR=1.09, 95% CI=1.02-1.15; AT vs. AA: OR=1.04, 95% CI=1.01-1.33). Meanwhile, we found that rs3750805 polymorphism could increased the risk for breast cancer (TT+AT vs. AA: OR=1.12, 95% CI=1.01-1.24).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates that TCF7L2 polymorphisms may increase the risk for breast cancer.
Keywords: TCF7L2; breast cancer; polymorphisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between TCF7L2 polymorphisms and risk of breast cancer among Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women: the Breast Cancer Health Disparities Study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Nov;136(2):593-602. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2299-7. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 23085767 Free PMC article.
-
TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Mar 31;14(1):2860-7. doi: 10.4238/2015.March.31.16. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 25867435
-
[Correlation between TCF7L2 gene polymorphism and genetic susceptibility in women with gestational diabetes mellitus].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;49(8):588-93. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25354859 Chinese.
-
Association between IL-1A (-889C/T) polymorphism and susceptibility of chronic periodontitis: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2020 Mar 1;729:144227. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144227. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31759990
-
Association between three eNOS polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(13):5317-24. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.13.5317. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25040995
Cited by
-
The Complex Connection Between Myocardial Dysfunction and Cancer Beyond Cardiotoxicity: Shared Risk Factors and Common Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 8;25(23):13185. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of metabolism-related genes polymorphisms with adenocarcinoma of the oesophagogastric junction: Evidence from 2261 subjects.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov;120(11):18689-18701. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29167. Epub 2019 Jun 18. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31211453 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic colocalization atlas points to common regulatory sites and genes for hematopoietic traits and hematopoietic contributions to disease phenotypes.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Jun 29;13(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-00742-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32600345 Free PMC article.
-
TCF7L2 rs7903146 polymorphism is associated with gastric cancer: A case-control study in the Venezuelan population.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 28;22(28):6520-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6520. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27605886 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular disease and cancer: Evidence for shared disease pathways and pharmacologic prevention.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Aug;263:343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28624099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Jensen OM, Esteve J, Moller H, Renard H. Cancer in the European Community and its member states. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26:1167–1256. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Foreman KJ, Delossantos AM, Lozano R, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, Naghavi M. Breast and cervical cancer in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2011;378:1461–1484. - PubMed
-
- Cancer incidence in five continents. Volume VII. IARC Sci Publ. 1997:i–xxxiv. 1–1240. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources