Electronic monitoring of orthopedic brace compliance
- PMID: 26310101
- PMCID: PMC4619370
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-015-0679-3
Electronic monitoring of orthopedic brace compliance
Abstract
Purpose: Brace compliance measurement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) has been the subject of a few recent studies. Various sensors have been developed to measure compliance. We have developed a temperature-based data logger-the Cricket-specifically for scoliosis braces, with associated custom software, that is embedded directly in the brace. The purpose of this study was to analyze patterns of brace wear and patient compliance among children with AIS using the Cricket.
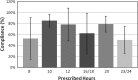
Methods: Fifty-five AIS patients prescribed various brace-time regimens were monitored using the Cricket. All subjects were treated with the Wilmington brace. The compliance rate for each group was determined.
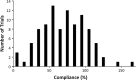
Results: Overall compliance among subjects was 69.9 ± 31.5 %. Only 14.5 % met or exceeded prescribed brace time. This is consistent with previous compliance monitoring results.
Conclusion: The results of this study objectively show the difference between prescribed and actual brace wear time and reaffirm the Cricket sensor as an accurate and comfortable brace-monitoring device.
Keywords: Bracing; Compliance; Electronic monitoring; Scoliosis.
Figures

References
-
- Lonstein JE, Winter RB. The Milwaukee brace for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. A review of one thousand and twenty patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76-A:1207–1221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

