Self-assembled DNA nanoclews for the efficient delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome editing
- PMID: 26310292
- PMCID: PMC4677991
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201506030
Self-assembled DNA nanoclews for the efficient delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome editing
Abstract
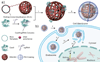
CRISPR-Cas9 represents a promising platform for genome editing, yet means for its safe and efficient delivery remain to be fully realized. A novel vehicle that simultaneously delivers the Cas9 protein and single guide RNA (sgRNA) is based on DNA nanoclews, yarn-like DNA nanoparticles that are synthesized by rolling circle amplification. The biologically inspired vehicles were efficiently loaded with Cas9/sgRNA complexes and delivered the complexes to the nuclei of human cells, thus enabling targeted gene disruption while maintaining cell viability. Editing was most efficient when the DNA nanoclew sequence and the sgRNA guide sequence were partially complementary, offering a design rule for enhancing delivery. Overall, this strategy provides a versatile method that could be adapted for delivering other DNA-binding proteins or functional nucleic acids.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; DNA; drug delivery; genome editing; nanoparticles.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




References
-
- Ran FA, Cong L, Yan WX, Scott DA, Gootenberg JS, Kriz AJ, Zetsche B, Shalem O, Wu X, Makarova KS, Koonin EV, Sharp PA, Zhang F. Nature. 2015;520:186–191. - PMC - PubMed
- Platt Randall J, Chen S, Zhou Y, Yim Michael J, Swiech L, Kempton Hannah R, Dahlman James E, Parnas O, Eisenhaure Thomas M, Jovanovic M, Graham Daniel B, Jhunjhunwala S, Heidenreich M, Xavier Ramnik J, Langer R, Anderson Daniel G, Hacohen N, Regev A, Feng G, Sharp Phillip A, Zhang F. Cell. 2014;159:440–455. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

