Loss of tapasin correlates with diminished CD8(+) T-cell immunity and prognosis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 26310568
- PMCID: PMC4551690
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-015-0647-1
Loss of tapasin correlates with diminished CD8(+) T-cell immunity and prognosis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Tapasin is a crucial component of the major histocompatibility (MHC) class I antigen presentation pathway. Defects in this pathway can lead to tumor immune evasion. The aim of this study was to test whether tapasin expression correlates with CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) infiltration of colorectal cancer (CRC) and overall survival.
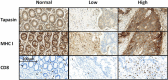
Methods: A next-generation tissue microarray (ngTMA) of 198 CRC patients with full clinicopathological information was included in this study. TMA slides were immunostained for tapasin, MHC I and CD8. Marker expression was analyzed with immune-cell infiltration, patient survival and TNM-staging.
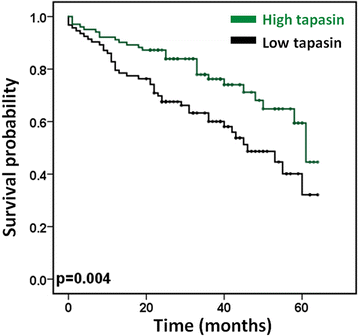
Results: A reduction of tapasin expression strongly correlated with venous invasion (AUC 0.682, OR 2.7, p = 0.002; 95% CI 1.7-5.0), lymphatic invasion (AUC 0.620, OR 2.0, p = 0.005; 95 % CI 1.3-3.3), distant metastasis (AUC 0.727, OR 2.9, p = 0.004; 95% CI 1.4-5.9) and an infiltrative tumor border configuration (AUC 0.621, OR 2.2, p = 0.017; 95% CI 1.2-4.4). Further, tapasin expression was associated with CD8(+) CTL infiltration (AUC 0.729, OR 5.4, p < 0.001; 95% CI 2.6-11), and favorable overall survival (p = 0.004, HR 0.6, 95% CI 0.42-0.85).
Conclusions: Consistent with published functional data showing that tapasin promotes antigen presentation, as well as tumor immune recognition and destruction by CD8(+) CTLs, a reduction in tapasin expression is associated with tumor progression in CRC.
Figures
References
-
- Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, Tosolini M, Camus M, Berger A, Wind P, Zinzindohoué F, Bruneval P, Cugnenc P-H, Trajanoski Z, Fridman W-H, Pagès F. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313:1960–1964. doi: 10.1126/science.1129139. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Berger A, Bindea G, Meatchi T, Bruneval P, Trajanoski Z, Fridman W-H, Pagès F, Galon J. Histopathologic-based prognostic factors of colorectal cancers are associated with the state of the local immune reaction. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:610–618. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.5425. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

