Hypoxia: a key player in antitumor immune response. A Review in the Theme: Cellular Responses to Hypoxia
- PMID: 26310815
- PMCID: PMC4628936
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00207.2015
Hypoxia: a key player in antitumor immune response. A Review in the Theme: Cellular Responses to Hypoxia
Abstract
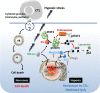
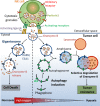
The tumor microenvironment is a complex system, playing an important role in tumor development and progression. Besides cellular stromal components, extracellular matrix fibers, cytokines, and other metabolic mediators are also involved. In this review we outline the potential role of hypoxia, a major feature of most solid tumors, within the tumor microenvironment and how it contributes to immune resistance and immune suppression/tolerance and can be detrimental to antitumor effector cell functions. We also outline how hypoxic stress influences immunosuppressive pathways involving macrophages, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, T regulatory cells, and immune checkpoints and how it may confer tumor resistance. Finally, we discuss how microenvironmental hypoxia poses both obstacles and opportunities for new therapeutic immune interventions.
Keywords: autophagy and antitumor immune response; cancer stem cells; circulating tumor cells; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factor; immune suppression; lymphoid cells; myeloid cells; programmed death-ligand 1; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Akalay I, Janji B, Hasmim M, Noman MZ, Andre F, De Cremoux P, Bertheau P, Badoual C, Vielh P, Larsen AK, Sabbah M, Tan TZ, Keira JH, Hung NT, Thiery JP, Mami-Chouaib F, Chouaib S. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and autophagy induction in breast carcinoma promote escape from T-cell-mediated lysis. Cancer Res 73: 2418–2427, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Akalay I, Tan TZ, Kumar P, Janji B, Mami-Chouaib F, Charpy C, Vielh P, Larsen AK, Thiery JP, Sabbah M, Chouaib S. Targeting WNT1-inducible signaling pathway protein 2 alters human breast cancer cell susceptibility to specific lysis through regulation of KLF-4 and miR-7 expression. Oncogene 34: 2261–2271, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Allavena P, Piemonti L, Longoni D, Bernasconi S, Stoppacciaro A, Ruco L, Mantovani A. IL-10 prevents the differentiation of monocytes to dendritic cells but promotes their maturation to macrophages. Eur J Immunol 28: 359–369, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

