Synthetic Small Molecule Inhibitors of Hh Signaling As Anti-Cancer Chemotherapeutics
- PMID: 26310919
- PMCID: PMC5062741
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867322666150827093904
Synthetic Small Molecule Inhibitors of Hh Signaling As Anti-Cancer Chemotherapeutics
Abstract
The hedgehog (Hh) pathway is a developmental signaling pathway that is essential to the proper embryonic development of many vertebrate systems. Dysregulation of Hh signaling has been implicated as a causative factor in the development and progression of several forms of human cancer. As such, the development of small molecule inhibitors of Hh signaling as potential anti-cancer chemotherapeutics has been a major area of research interest in both academics and industry over the past ten years. Through these efforts, synthetic small molecules that target multiple components of the Hh pathway have been identified and advanced to preclinical or clinical development. The goal of this review is to provide an update on the current status of several synthetic small molecule Hh pathway inhibitors and explore the potential of several recently disclosed inhibitory scaffolds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures





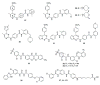


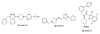



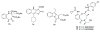
Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Developmental Signaling Pathway Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2015;22(35):4031-2. doi: 10.2174/092986732235151126193822. Curr Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26630931 No abstract available.
-
Discovery of Hedgehog Antagonists for Cancer Therapy.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(19):2033-2058. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170316115500. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28302010 Review.
-
Hedgehog pathway agonism: therapeutic potential and small-molecule development.ChemMedChem. 2014 Jan;9(1):27-37. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201300358. Epub 2013 Nov 7. ChemMedChem. 2014. PMID: 24203435 Review.
-
Current Status of Hedgehog Signaling Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(3):243-258. doi: 10.2174/0115680266280850231221074340. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38231069 Review.
-
Development of anticancer agents targeting the Hedgehog signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Aug;74(15):2773-2782. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2497-x. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28314894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Formulation and evaluation of itraconazole liposomes for Hedgehog pathway inhibition.J Liposome Res. 2020 Sep;30(3):305-311. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2019.1668011. Epub 2019 Oct 2. J Liposome Res. 2020. PMID: 31576768 Free PMC article.
-
A structurally guided dissection-then-evolution strategy for ligand optimization of smoothened receptor.Medchemcomm. 2017 Apr 28;8(6):1332-1336. doi: 10.1039/c7md00104e. eCollection 2017 Jun 1. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 30108845 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Hydantoin-Cored Ligands for Smoothened Receptor.ChemistryOpen. 2021 Oct;10(10):1028-1032. doi: 10.1002/open.202100216. ChemistryOpen. 2021. PMID: 34648230 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing the Clinically Efficacious Antifungal Agent Itraconazole as an Anticancer Chemotherapeutic.J Med Chem. 2016 Apr 28;59(8):3635-49. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01718. Epub 2016 Apr 6. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27014922 Free PMC article.
-
The role of bone marrow microenvironment (BMM) cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression: immune checkpoints, metabolic checkpoints, and signaling pathways.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 21;21(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01282-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37735675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amakye D, Jagani Z, Dorsch M. Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Med. 2013;19:1410–1422. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Thérond PP. The mechanisms of hedgehog signaling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:416–429. - PubMed
-
- Trinh TN, McLaughlin EA, Gordon CP, McCluskey A. Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors as cancer suppressing agents. Med Chem Commun. 2014;5:117–133.
-
- Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Scott MP. Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science. 2007;317:372–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

