Synthetic Small Molecule Inhibitors of Hh Signaling As Anti-Cancer Chemotherapeutics
- PMID: 26310919
- PMCID: PMC5062741
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867322666150827093904
Synthetic Small Molecule Inhibitors of Hh Signaling As Anti-Cancer Chemotherapeutics
Abstract
The hedgehog (Hh) pathway is a developmental signaling pathway that is essential to the proper embryonic development of many vertebrate systems. Dysregulation of Hh signaling has been implicated as a causative factor in the development and progression of several forms of human cancer. As such, the development of small molecule inhibitors of Hh signaling as potential anti-cancer chemotherapeutics has been a major area of research interest in both academics and industry over the past ten years. Through these efforts, synthetic small molecules that target multiple components of the Hh pathway have been identified and advanced to preclinical or clinical development. The goal of this review is to provide an update on the current status of several synthetic small molecule Hh pathway inhibitors and explore the potential of several recently disclosed inhibitory scaffolds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures





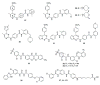


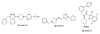



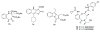
References
-
- Amakye D, Jagani Z, Dorsch M. Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Med. 2013;19:1410–1422. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Thérond PP. The mechanisms of hedgehog signaling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:416–429. - PubMed
-
- Trinh TN, McLaughlin EA, Gordon CP, McCluskey A. Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors as cancer suppressing agents. Med Chem Commun. 2014;5:117–133.
-
- Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Scott MP. Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science. 2007;317:372–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

